Renal
Learning Objectives:
Describe the indications and limitations of US of the kidneys and bladder
Perform US to evaluate the urinary tract
Identify relevant US anatomy including the renal cortex, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, liver, spleen, and uterus or prostate
Recognize the relevant findings and pitfalls when evaluating for hydronephrosis, renal calculi, renal masses, bladder volume, pregnancy, and Foley catheter evaluation
Indications:
Flank pain
Back pain
Abdominal pain
Hematuria
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute Renal Failure/Acute Kidney Injury
Extended Indications:
Infection/abscess of the kidney
Gross bladder/prostate abnormalities
Foley cather placement/confirmation/evaluation
Required Views:
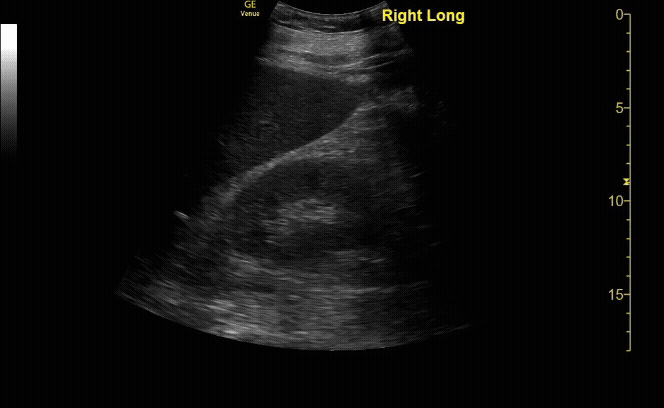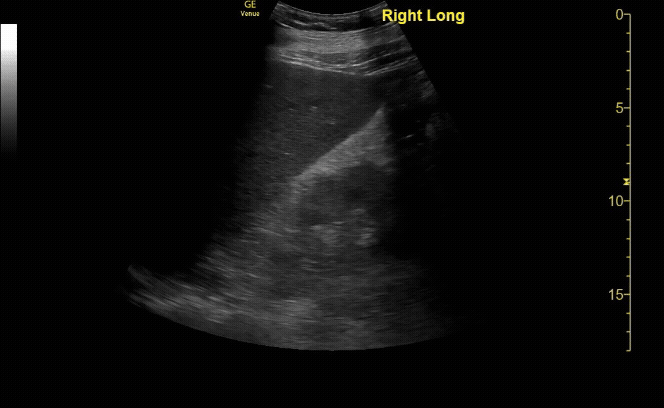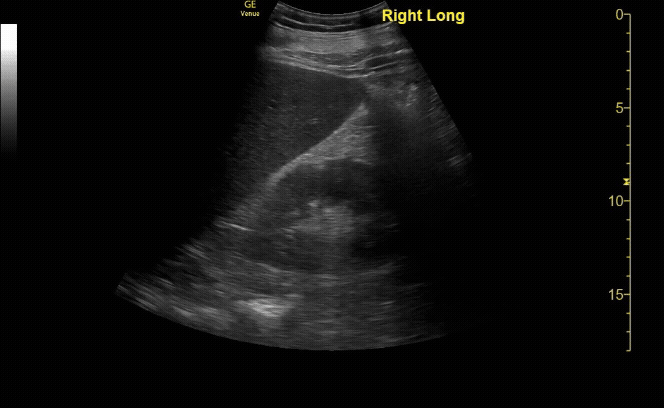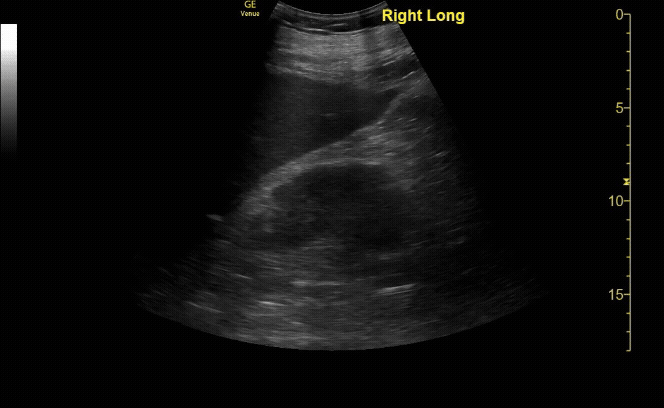
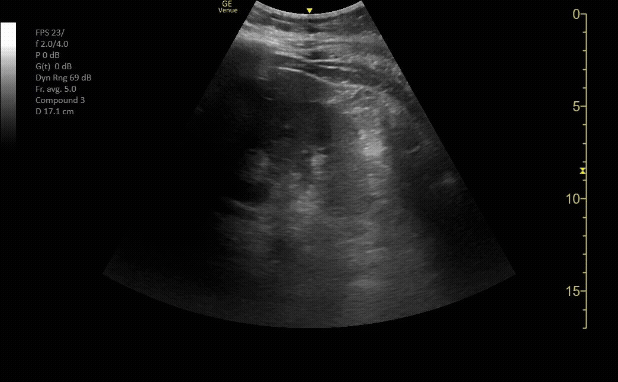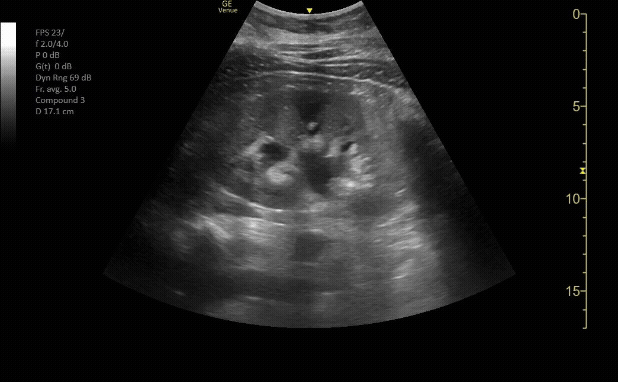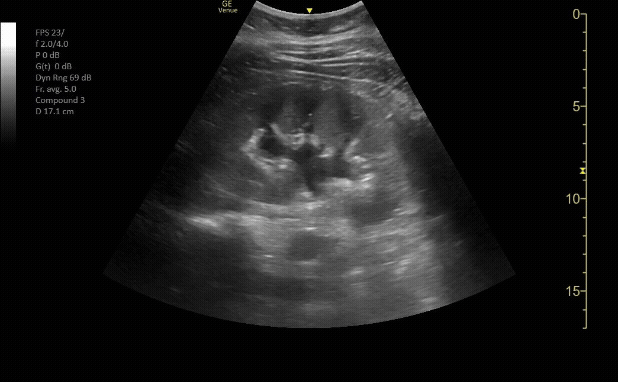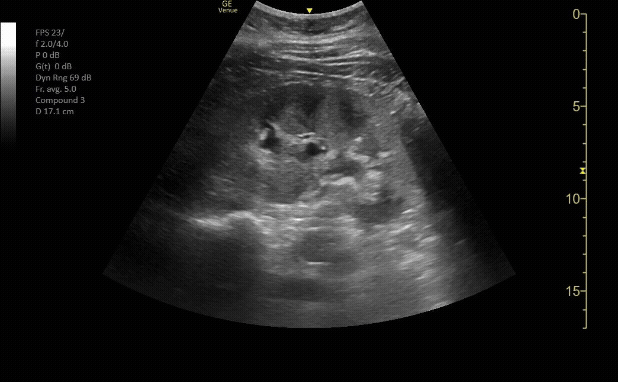
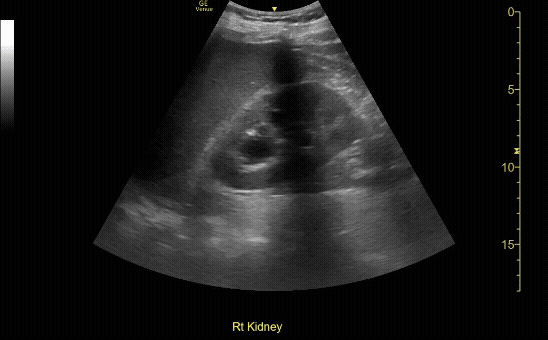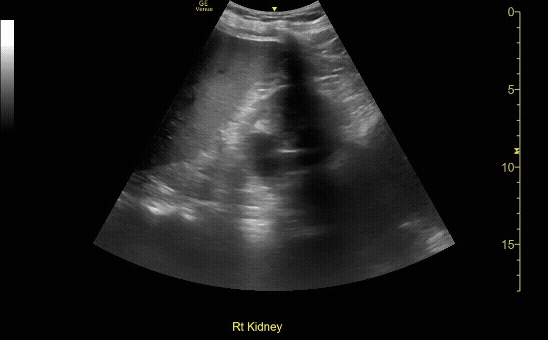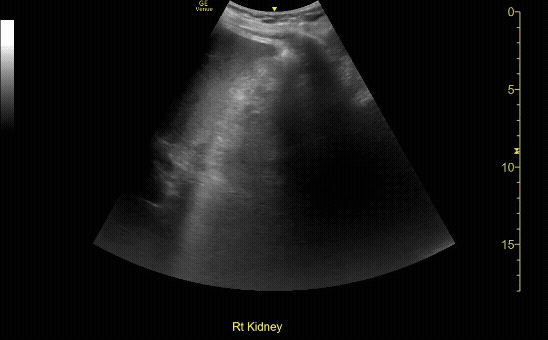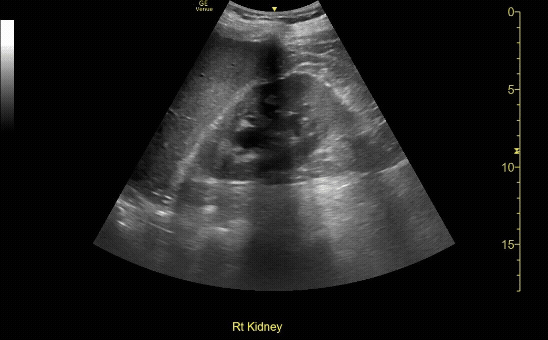
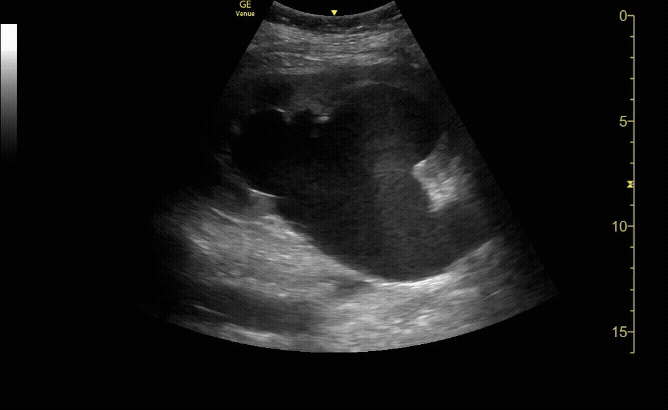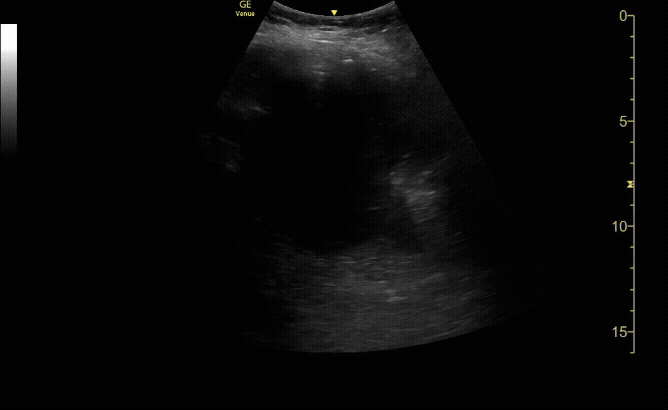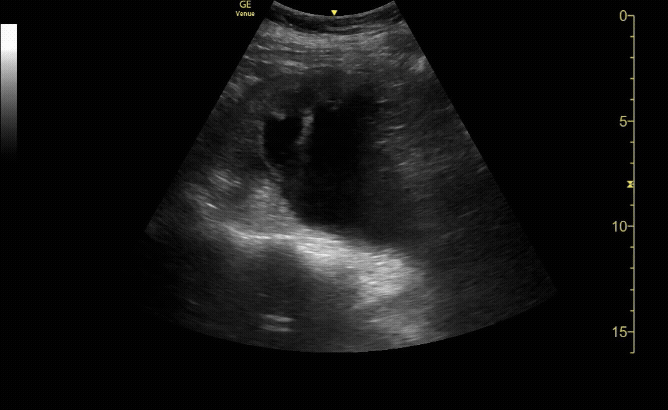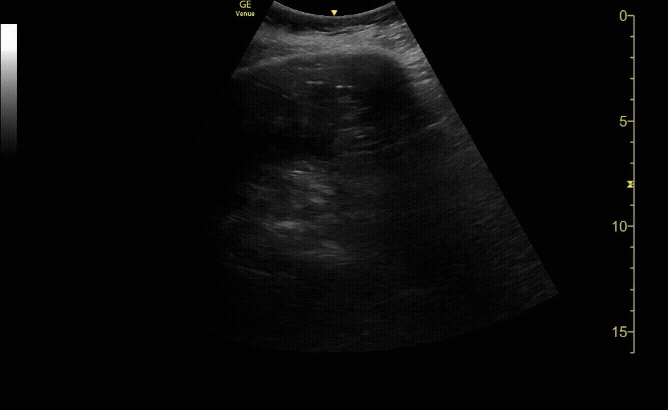
R/L kidney In sagittal (long) view
c/o Victoria Gonzalez, MD
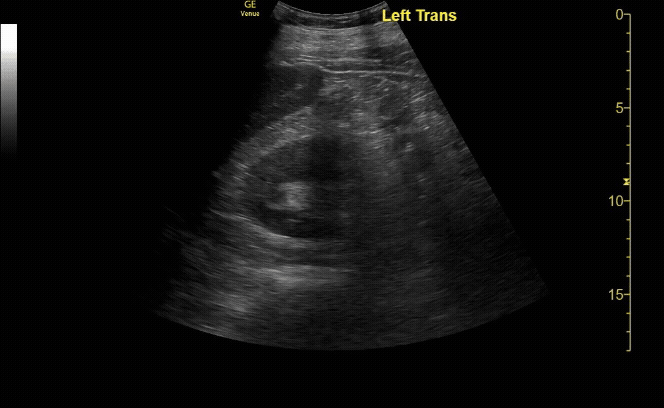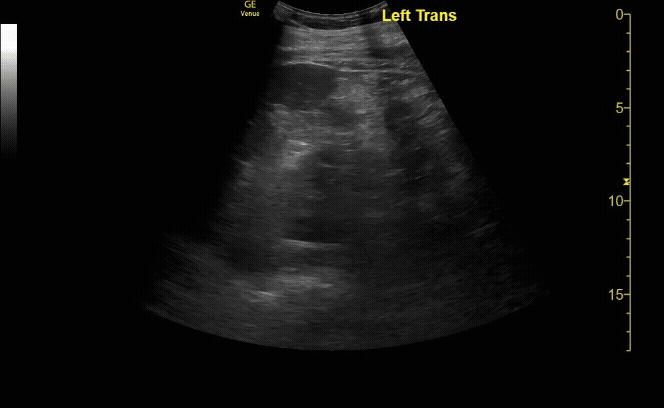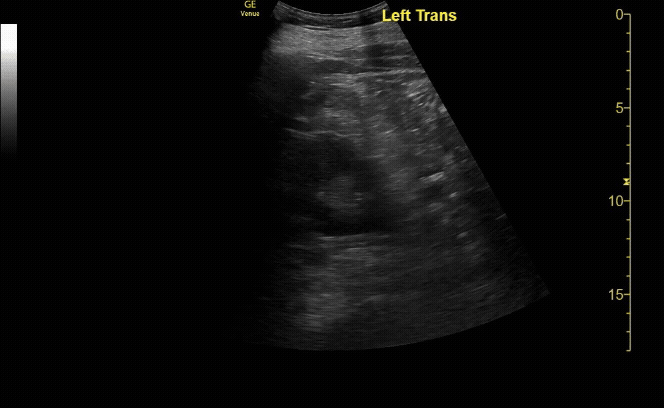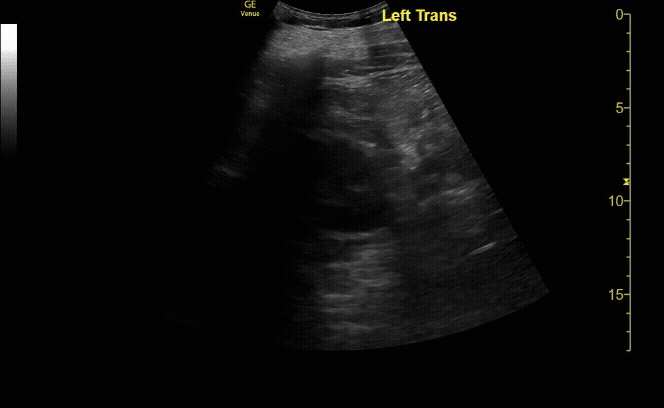
R/L kidney In transverse (short) view
c/o Victoria Gonzalez, MD
Bladder in transverse view
c/o Erica Dolph, MD
Bladder in sagittal view
c/o Erica Dolph, MD
How to Scan:
ACEP Sonoguide: Renal Ultrasound
Core Ultrasound: Genitourinary
POCUS 101: Renal Ultrasound Made Easy
Tips/Tricks/Pitfalls:
Hydronephrosis is commonly seen in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
Hydronephrosis can be masked by dehydration - a fluid bolus can make assessment easier
Mimics of hydronephrosis - vasculature and prominent medullary pyramids
Use color doppler to distinguish vasculature from hydronephrosis
Use color doppler over the ureteral jets to check for obstruction
Consider scanning the aorta in older patients with flank pain
Pathology:
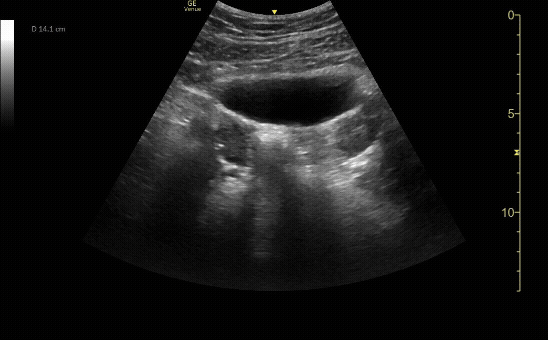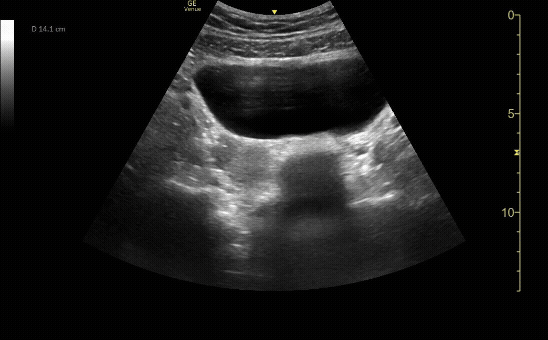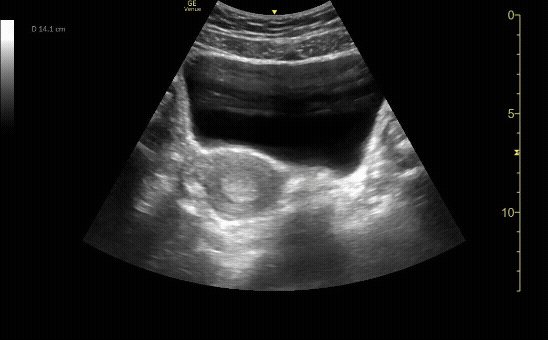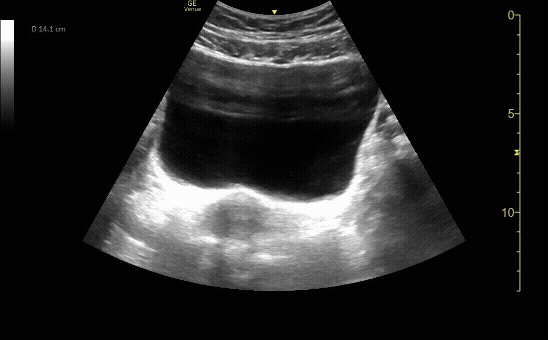
Mild Hydronephroiss in sagittal (long) view
c/o Taylor Wahrenbrock, MD
Moderate Hydronephrosis in sagittal( long) view
c/o Evanna Lerouge, MD
Severe Hydronephrosis in sagittal (long) view
c/o Jordyn Cohen, MD
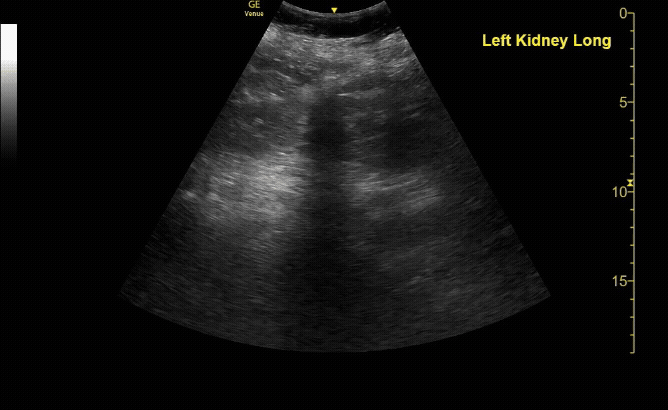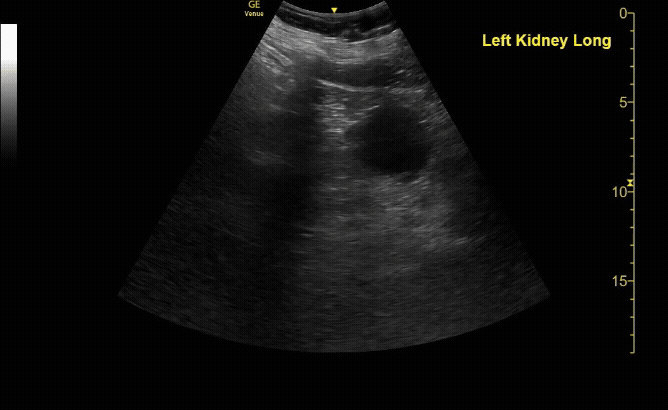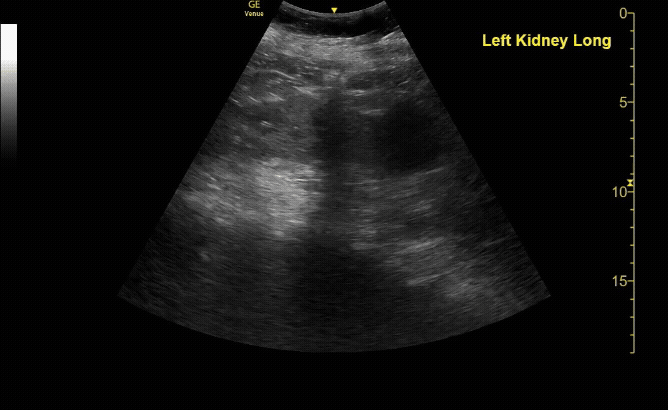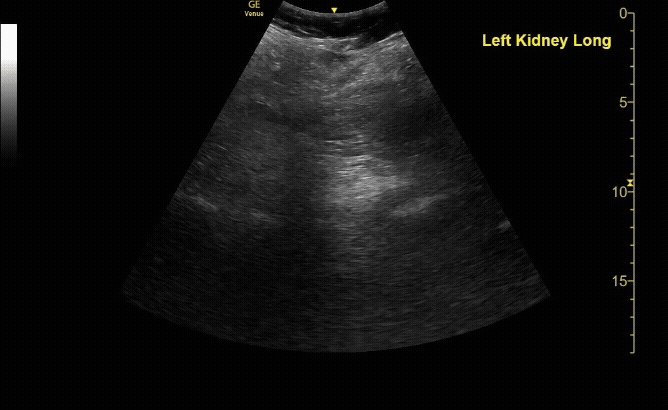
Renal Cyst in sagittal (long) view
c/o Vladimir Bernstein, MD
Key Literature:
Gaspari & Horst, Emergency Ultrasound and Urinalysis for Flank Pain
Smith-Bindman et al, Ultrasound vs CT for Suspected Nephrolithiasis
Pathan, et al, EM Physician Identification and Grading of Hydronephrosis Compared with Radiologists
Additional Resources:
Malin and Dawson iBook Volume 1, Chapter 6: Renal
ACEP Emergency Ultrasound Imaging Criteria Compendium Pages 12-15
AEUS Lecture by Peregrine Dalziel
Renal Ultrasound Lecture by Geoff Hayden
Author: Victoria Gonzalez, MD FDP-AEMUS