Ocular
Learning Objectives:
Describe the indications, limitations, and relative contraindications of ocular US
Perform bedside US protocol for evaluation of basic and advanced indications
Identify relevant US anatomy of orbital structures
Indications:
Vitreous hemorrhage
Posterior vitreous detachment
Retinal detachment
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurement
Optic disc evaluation
Extended Indications:
Lens dislocation
Intraocular Foreign Body
Central retinal artery / vein occlusion
Light reflex
Required Views:
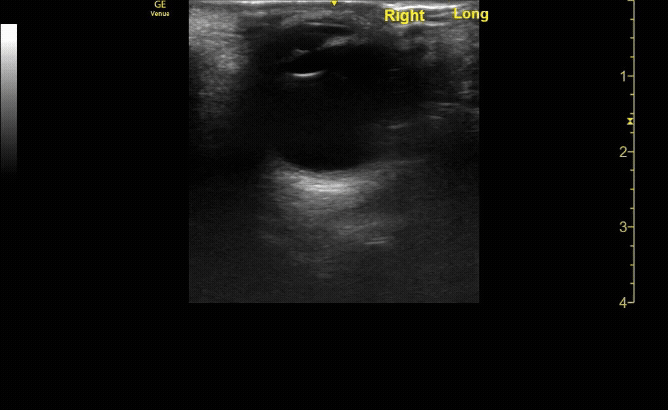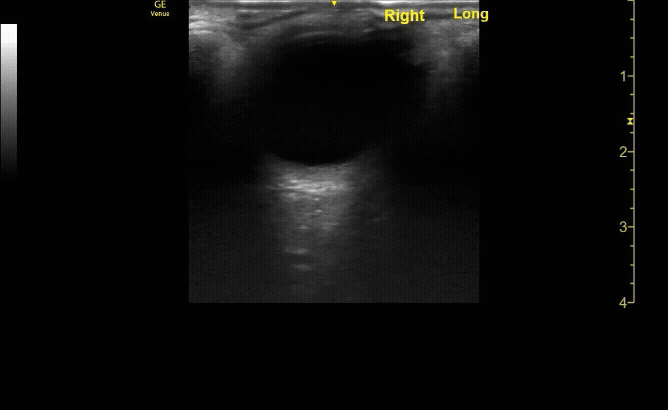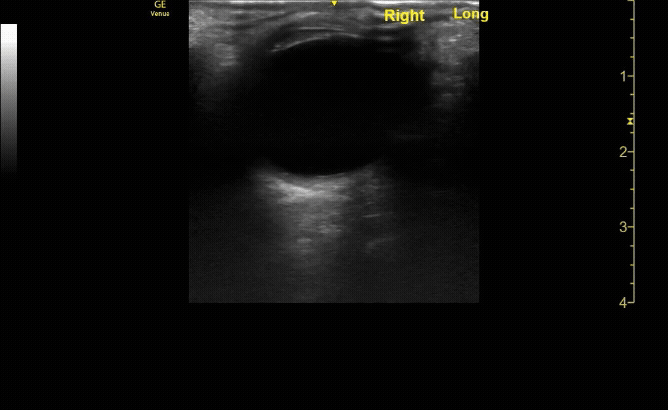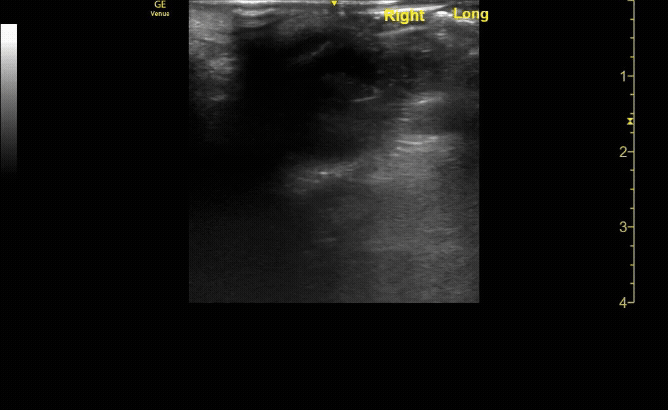
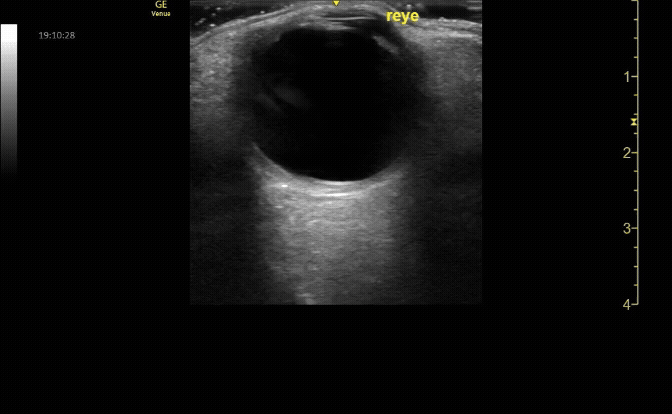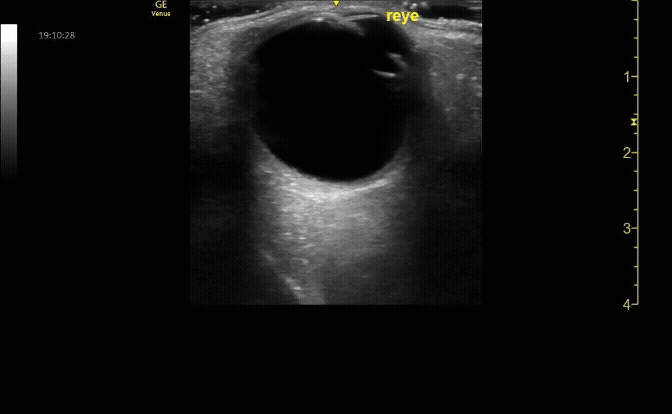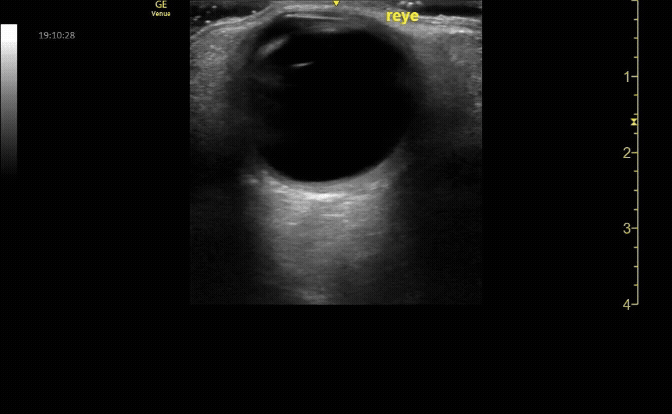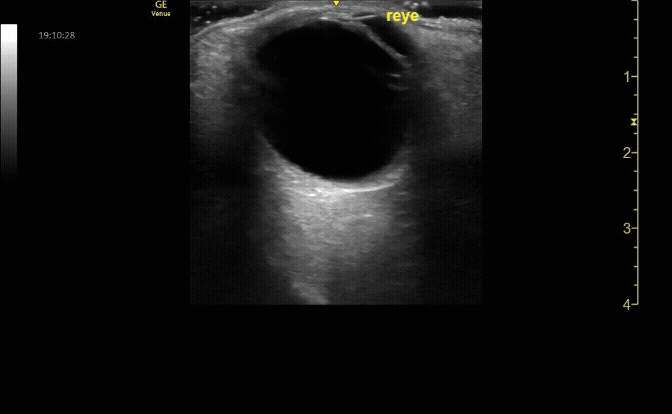
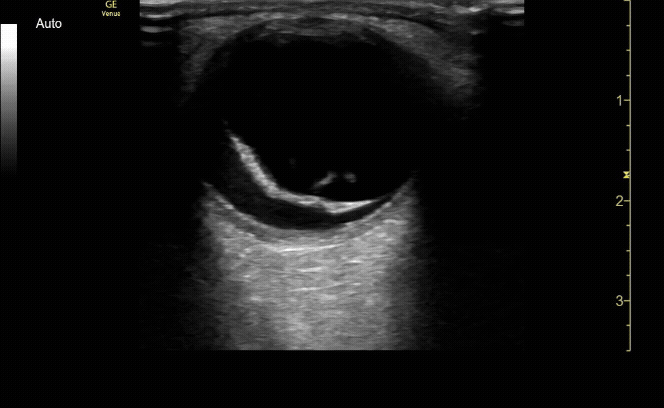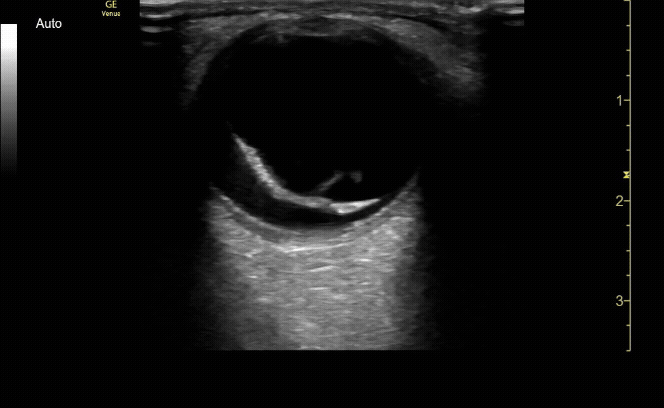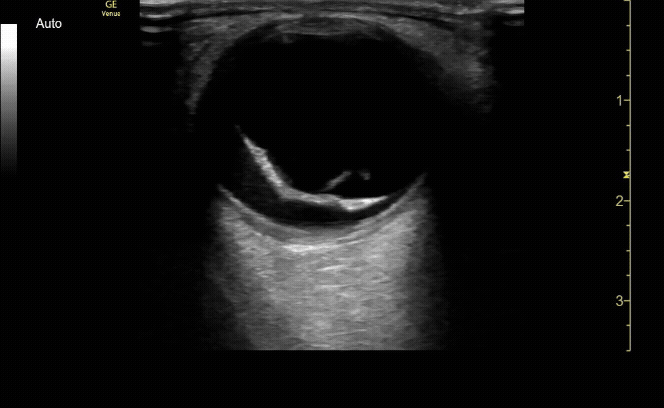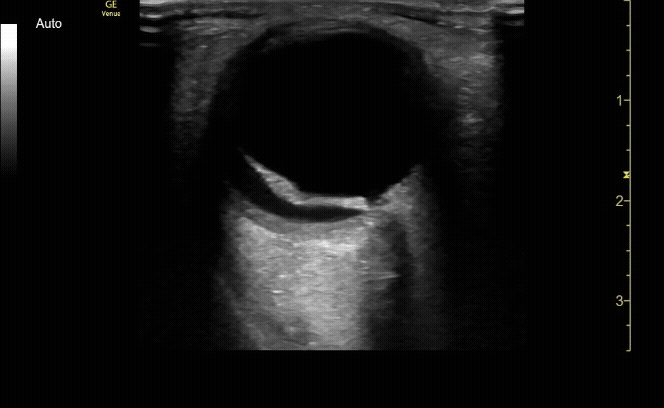
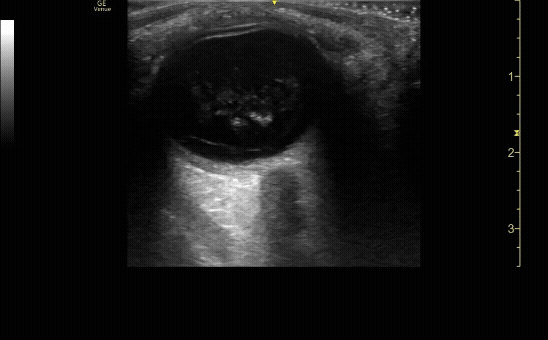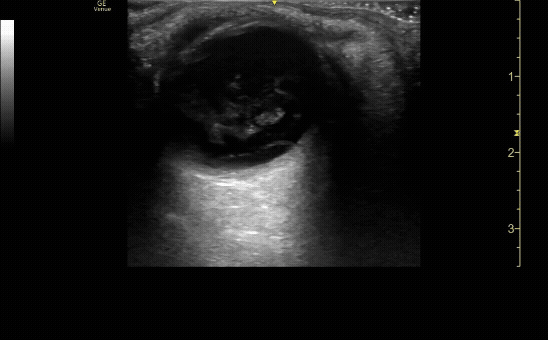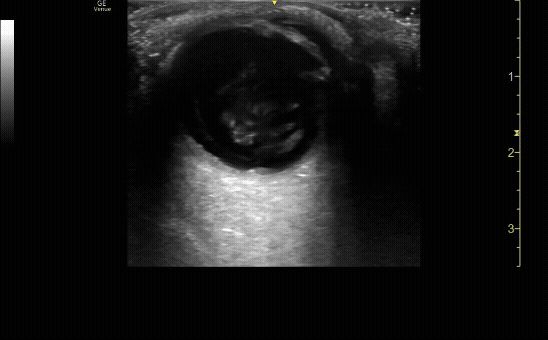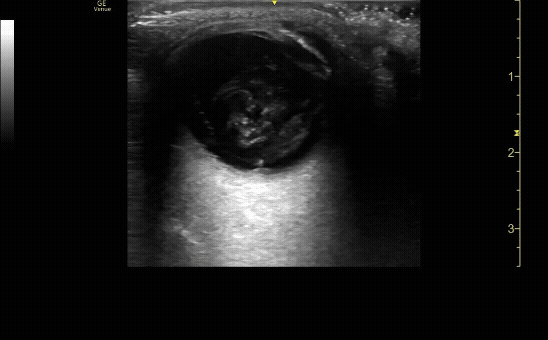
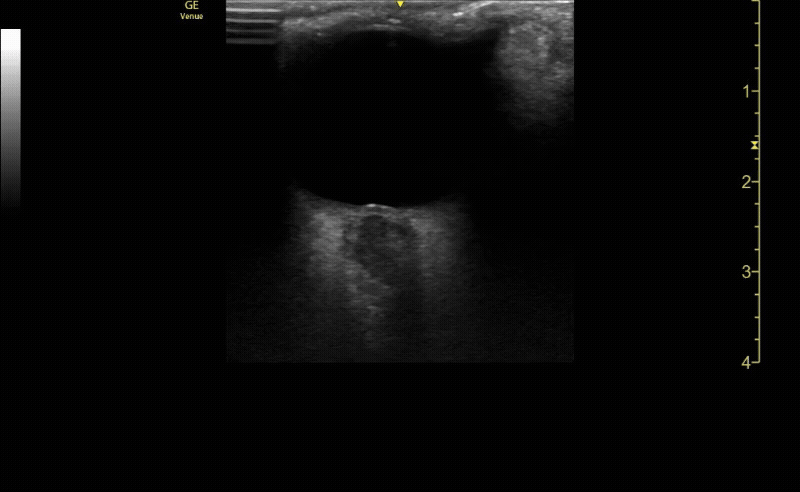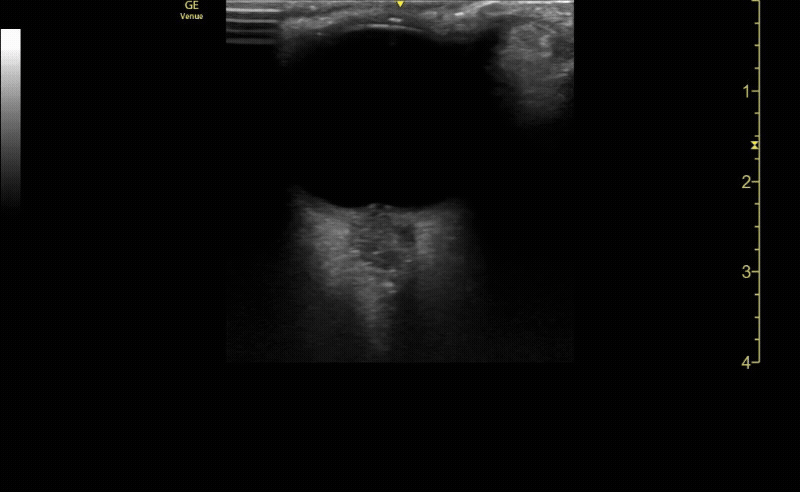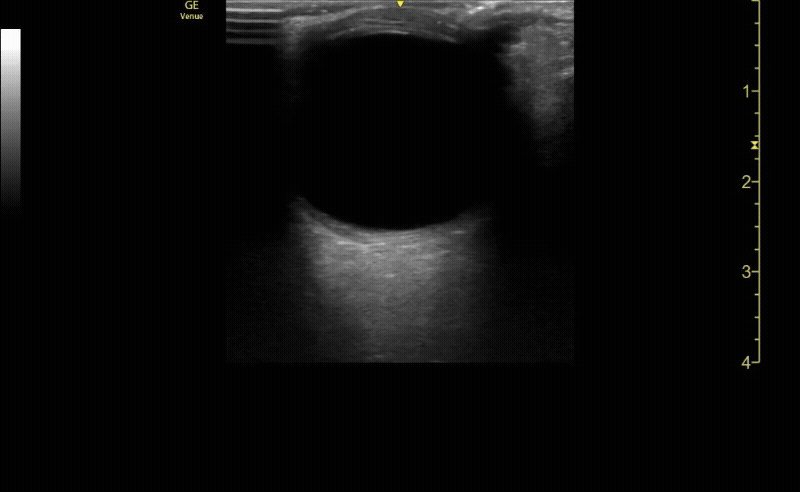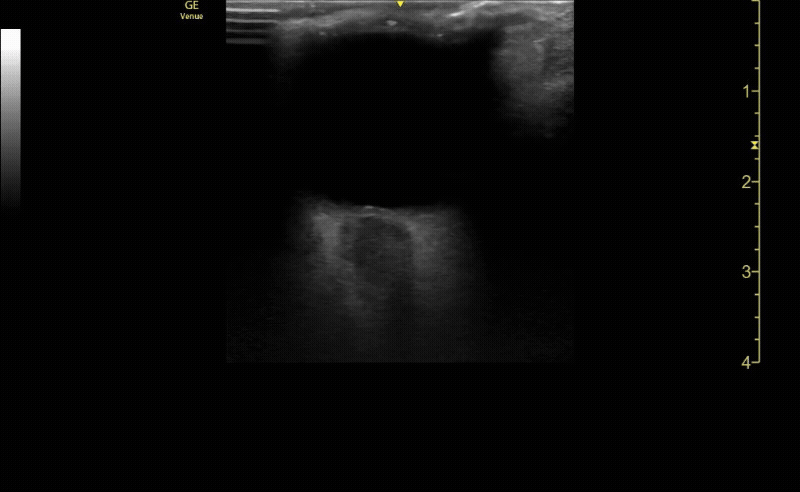
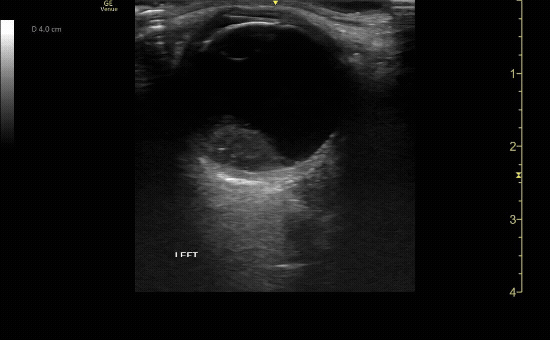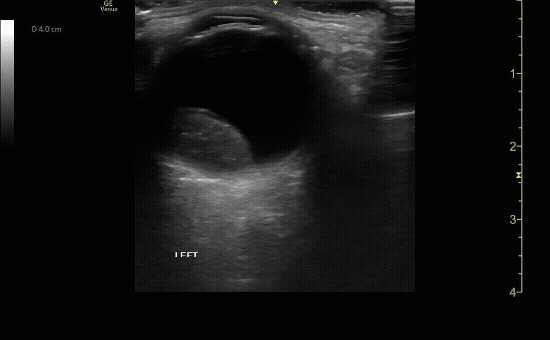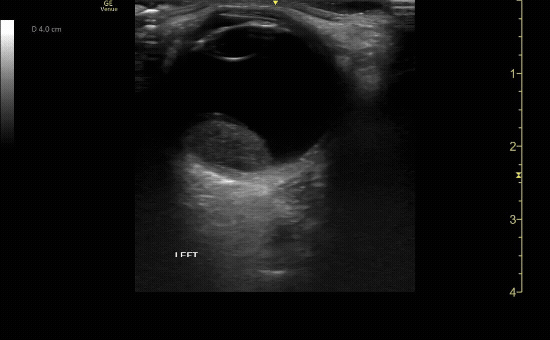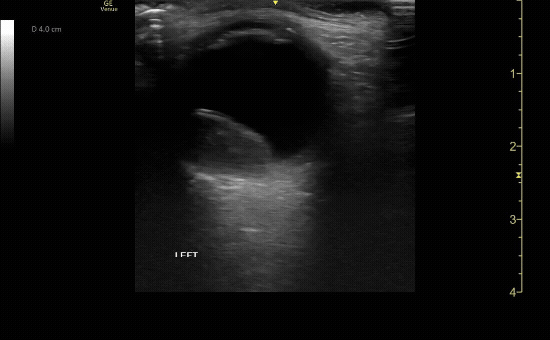
Transverse (short) view of the right eye. Ensure to scan both right and left for credit.
c/o Victoria Gonzalez, MD
Sagittal (long) view of the right eye. Ensure to scan both right and left for credit.
c/o Victoria Gonzalez
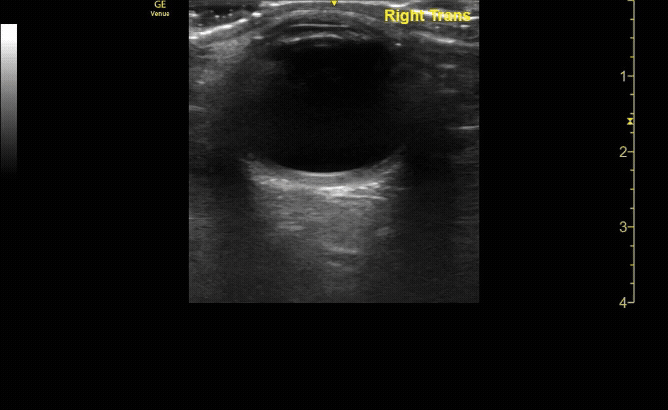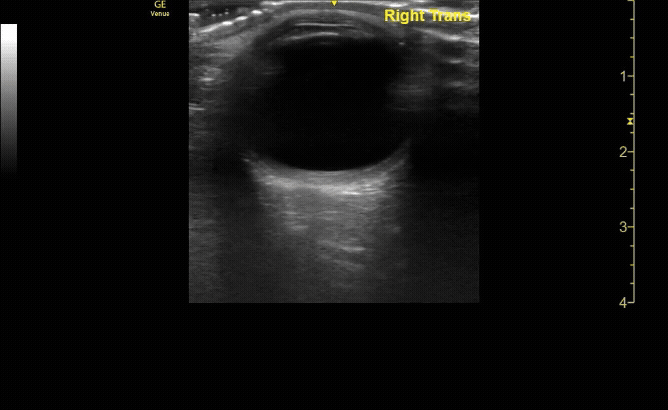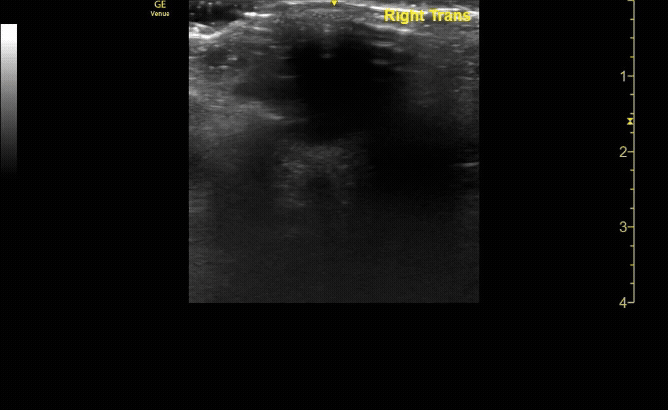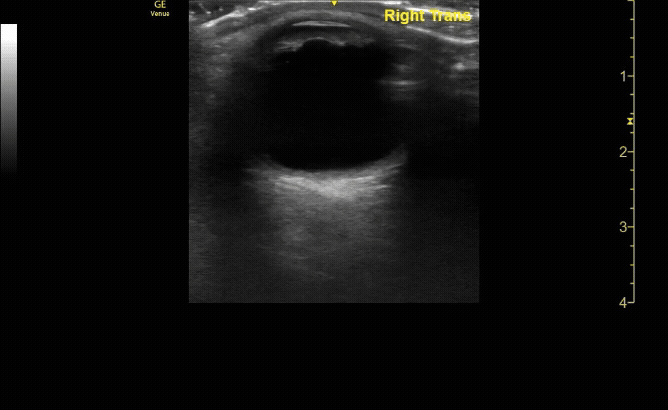
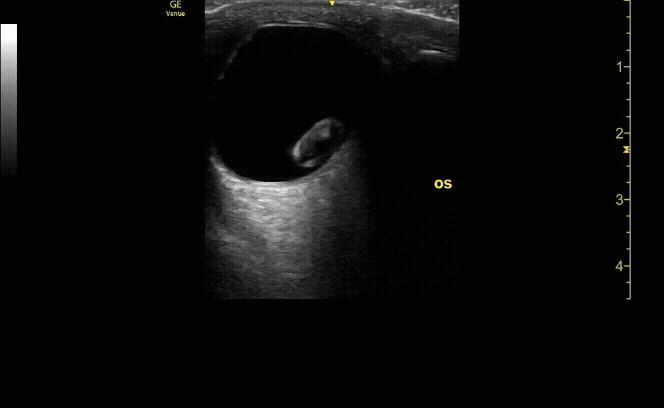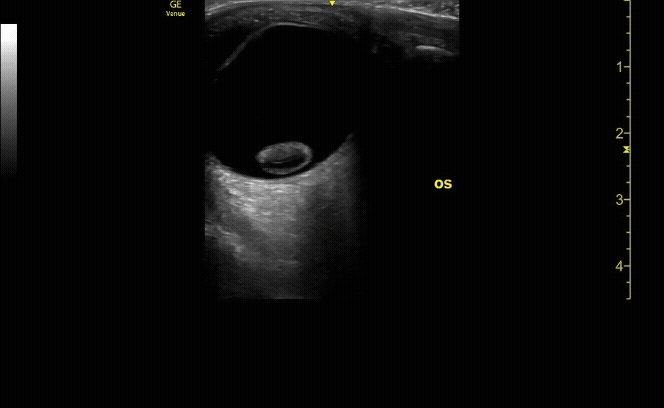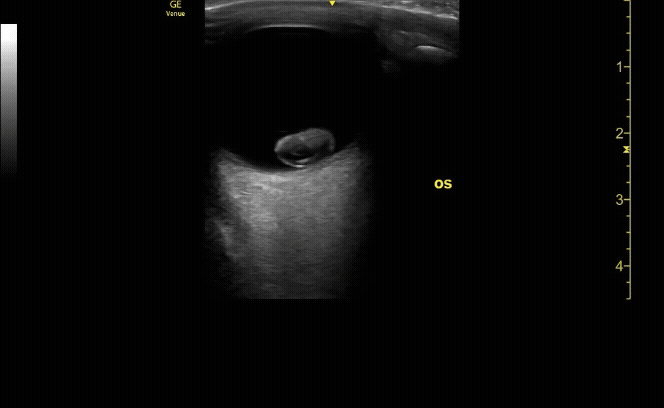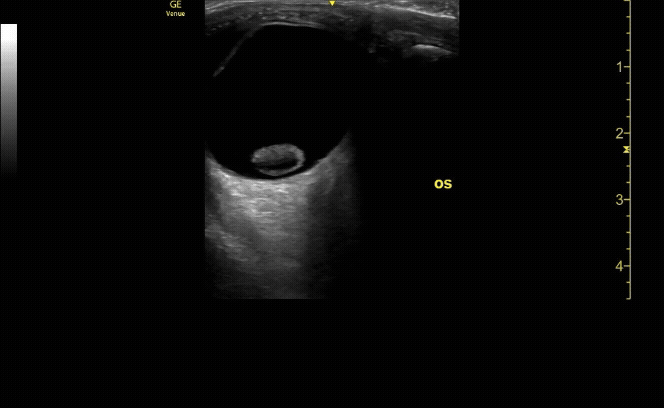
Measure the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) 3mm from the back of the eye. The ONSD should measure <5mm across.
c/o John Elue, MD
Evaluate the eye with ocular ultrasound as the patient moves their eye(s) left/right/up/down.
c/o John Elue, MD
How to Scan:
ACEP Sonoguide - Ocular Emergencies
Tips/Tricks/Pitfalls:
Probe marker should point toward the temple (this is the side of the macula)
Anchor your hand/pinky on a bony structure of the patient’s face to avoid placing too much pressure on the eye
Use copious amounts of US gel and minimal direct pressure on the eye
The retina is attached at the ora serrata and the optic nerve
Retinal detachment may be distinguished from posterior vitreous detachment because the retina is a thicker structure and is tethered at the ora serrata and the optic nerve
Remember the 3x5 iindex card rule to remember ONSD measurement (measure 3mm posterior to retina, <5mm across is normal)
Ocular US is relatively contraindicated if you suspect globe rupture or if there are periorbital wounds
Use oculokinetics (ask the patient move their eye during your US) to reveal vital information and ensure you don’t miss pathology
Pathology:
Mac off retinal detachment. Retina tethered at optic nerve.
c/o Melissa Hoshizaki, MD
CRAO with Intra-arterial spot sign (hyperechoic spot) in optic nerve.
c/o Susan Mari, MD
Vitreous hemorrhage displaying “washing machine” sign.
c/o Rayyan Kadi, MD
Lens dislocation
c/o Tim Wyman, MD
Dilated ONSD (7.6mm) with cupping in a patient with optic neuritis.
c/o Adrian Roblesi, MD
Ocular metastasis
c/o Kevin Boubouleix, MD
Key Literature:
Blaivas M. Bedside ultrasound in the evaluation of ocular pathology
Yoonessi, R., et al. Ocular ultrasound for retinal detachment
Tjahjadi, N. S., et al. POCUS of ONSD to detect elevated ICP in neurocritically ill patients
Wilson, Casey L., et al. Novice emergency medicine physician ultrasound of ONSD for papilledema
Additional Resources:
Malin and Dawson iBook Volume 2, Chapter 16: Ocular
ACEP Emergency Ultrasound Imaging Criteria Compendium Pages 21-25
Author: Susan Mari, MD (Class of 2026)
Reviewed by: Victoria Gonzalez, MD FDP-AEMUS