MSK/Soft Tissue
Learning Objectives:
Describe the indications and limitations of US of MSK structures
Perform US to evaluate various MSK pathologies
Identify relevant US anatomy, structures of common indications (skin/soft tissues, tendon rupture, tenosynovitis, joint effusion, fractures)
Recognize the relevant findings and pitfalls when evaluating for soft tissue infections, fractures, abscesses and other MSK scans
Indications:
Tendon/ligamentous tears or tendonitis
Inflammation or fluid (effusions) within the bursae and joints
Abscess/Cellulitis/Necrotizing fasciitis
Foreign bodies in the soft tissues (such as splinters or glass)
Fractures or dislocations
Extended indications:
Confirmation of joint dislocation/reduction
Diagnosis of fracture
Required Views:
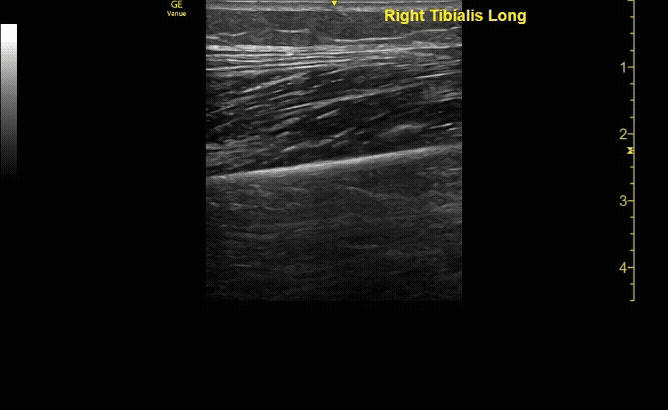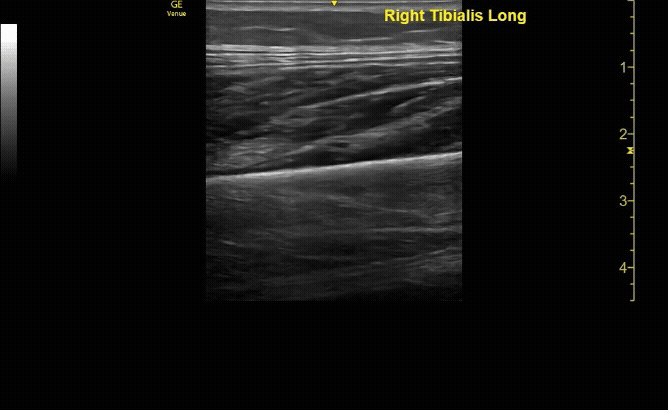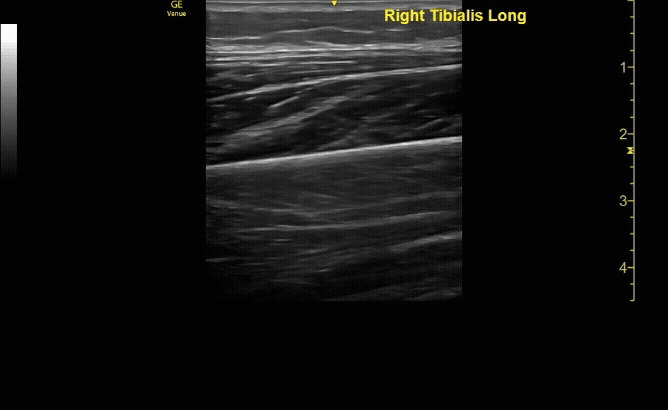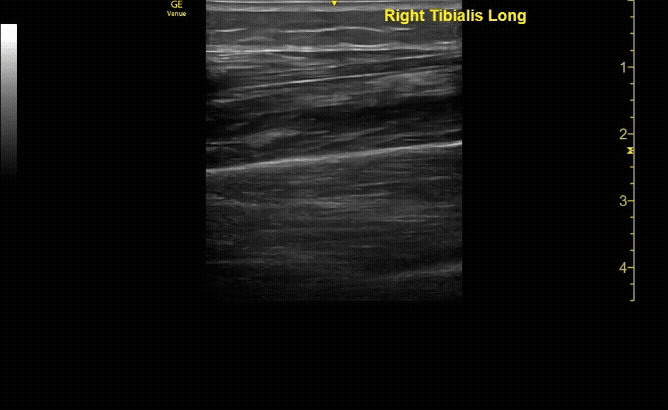
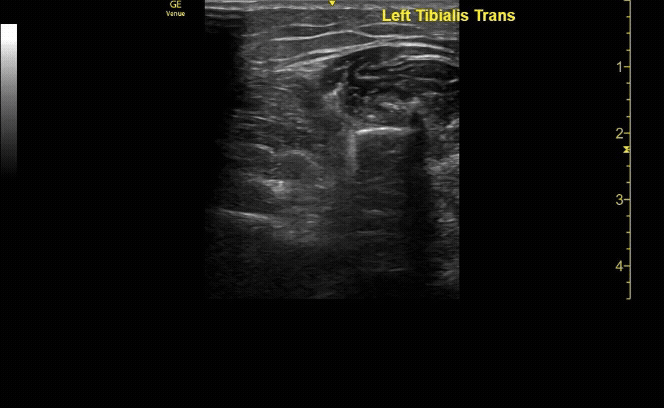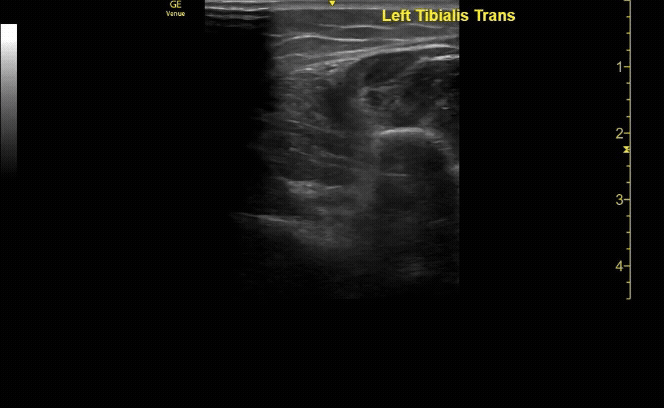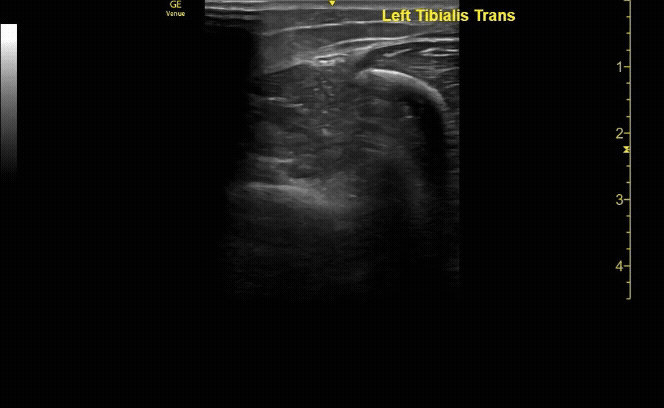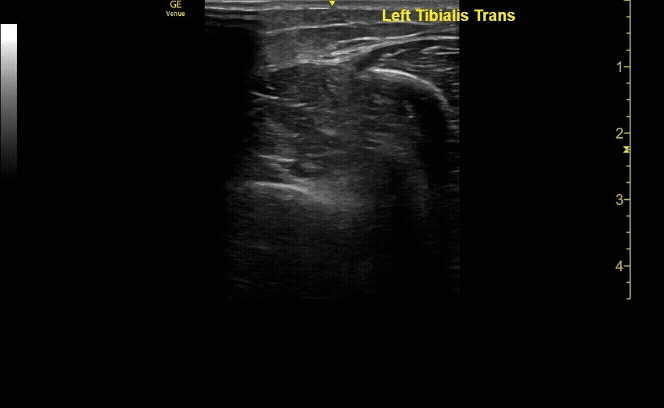
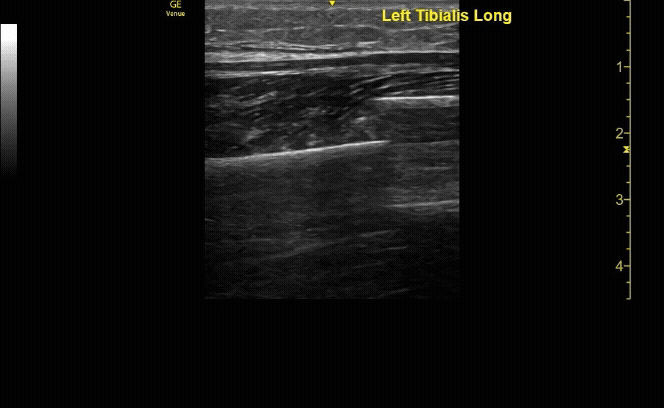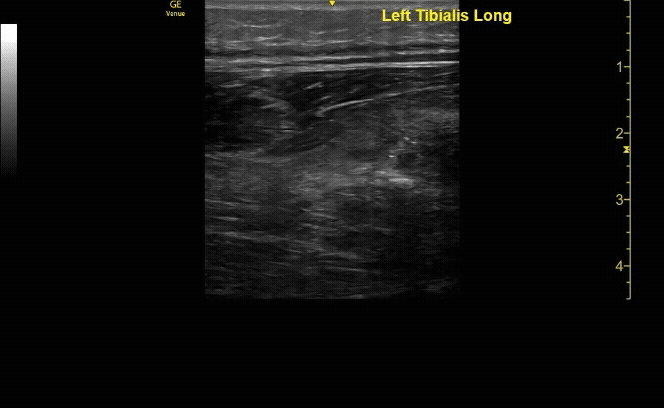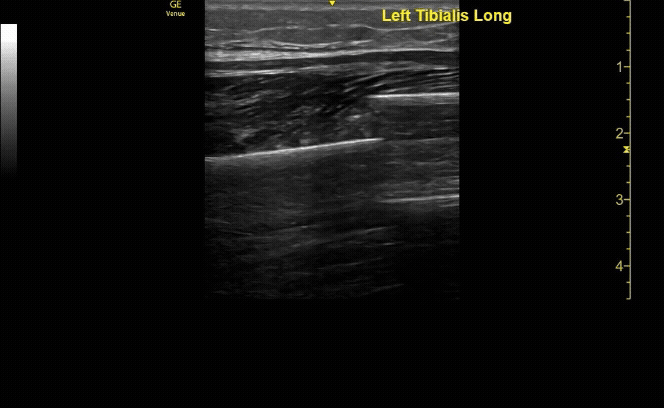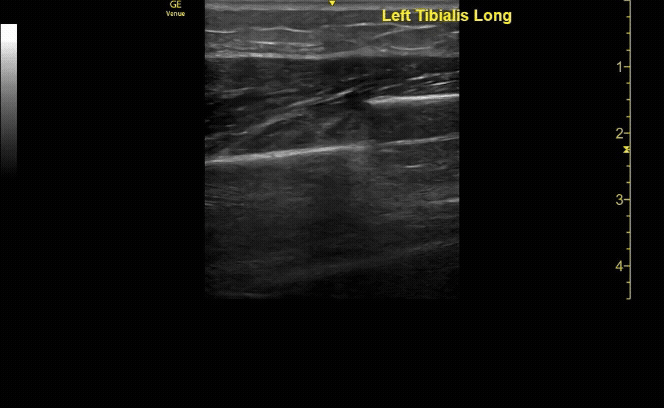
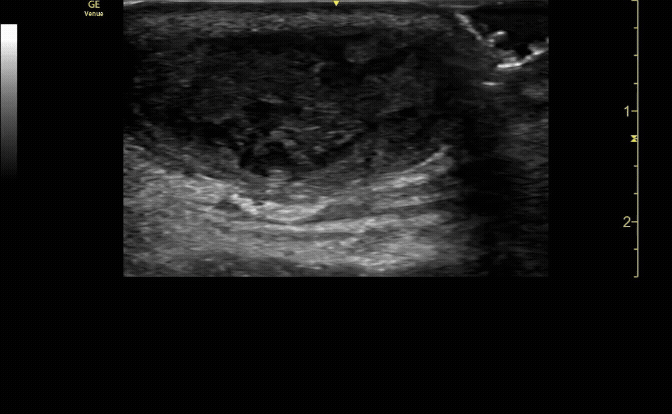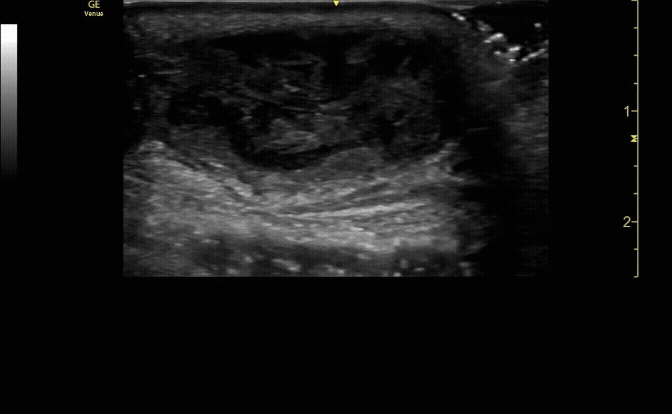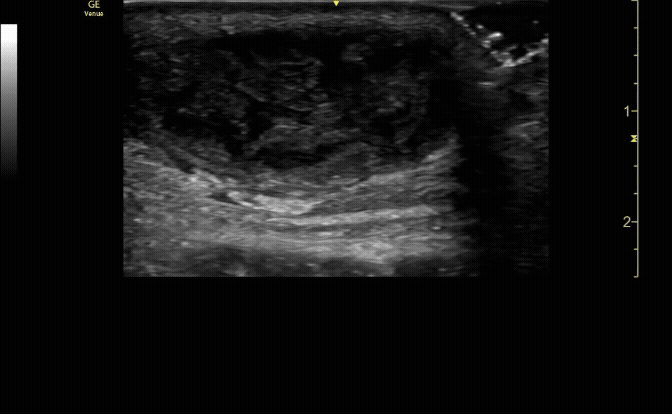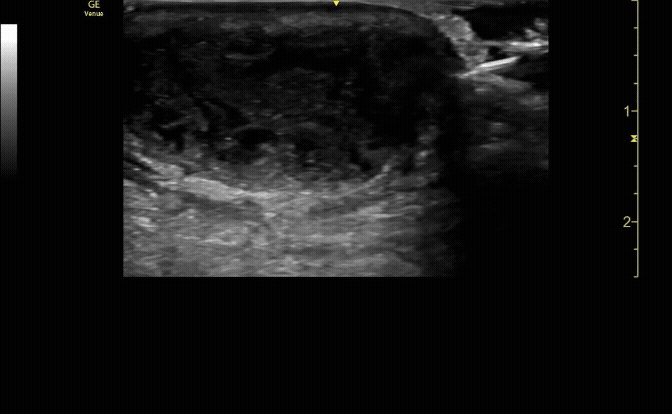
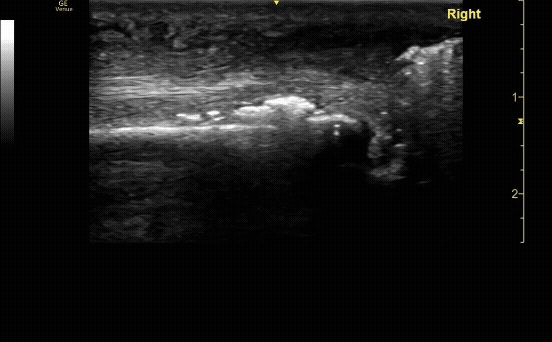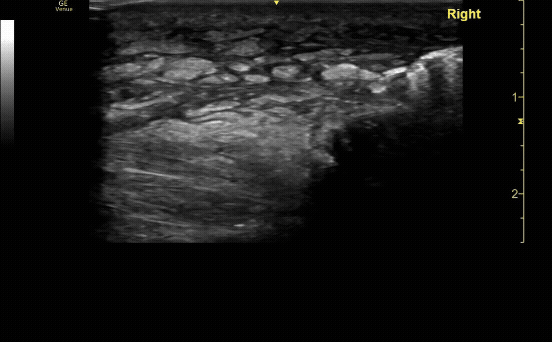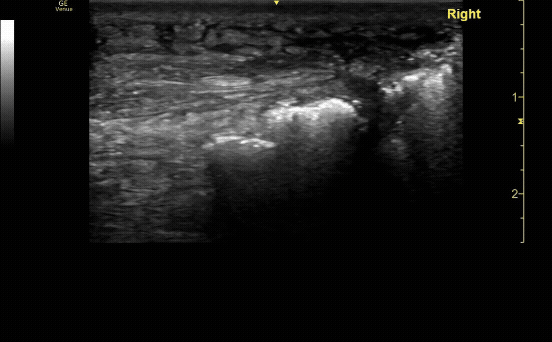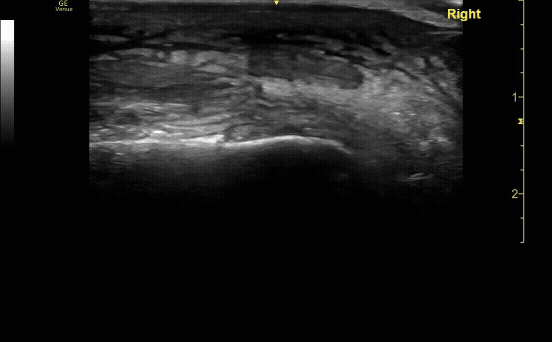
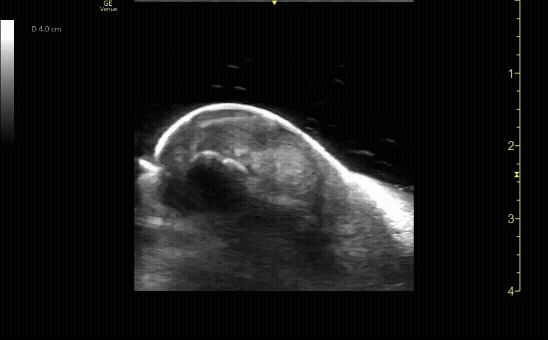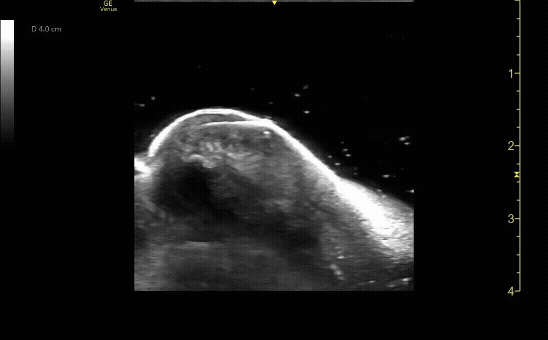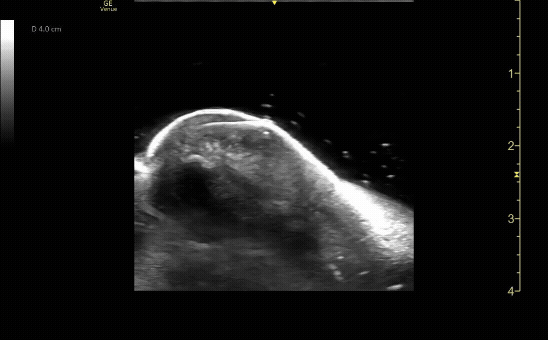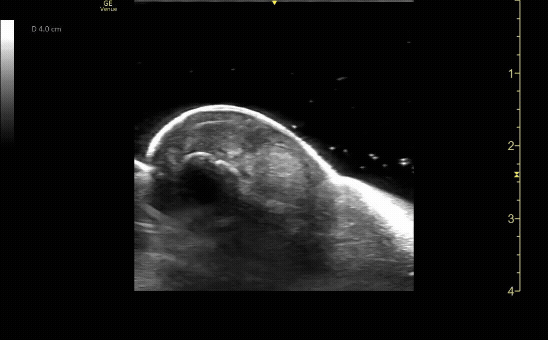
Unaffected tibia in transverse view.
c/o Santiago Tovar, MD
Unaffected tibia in sagittal view.
c/o Santiago Tovar, MD
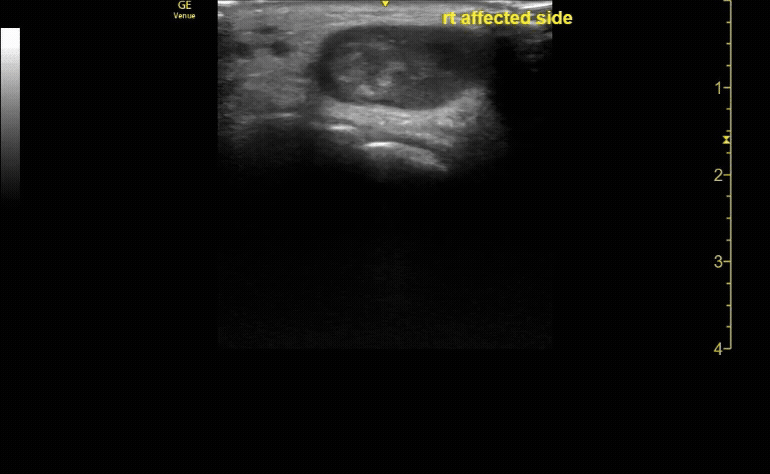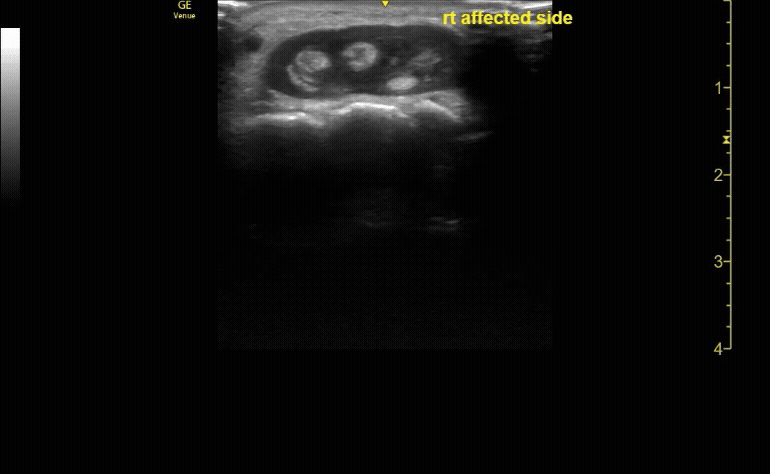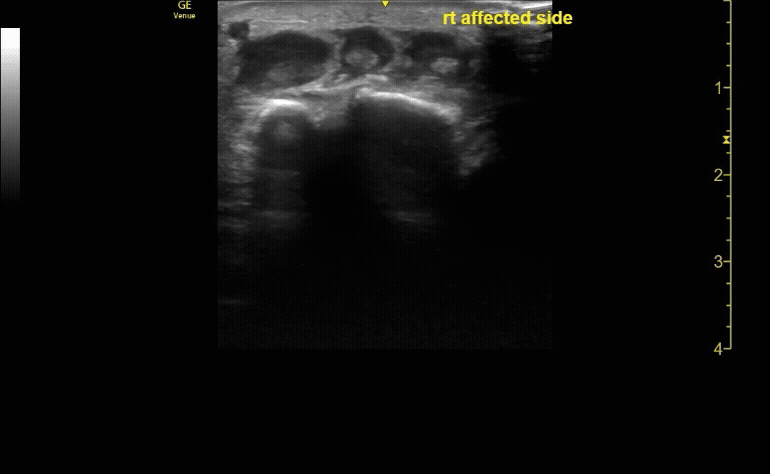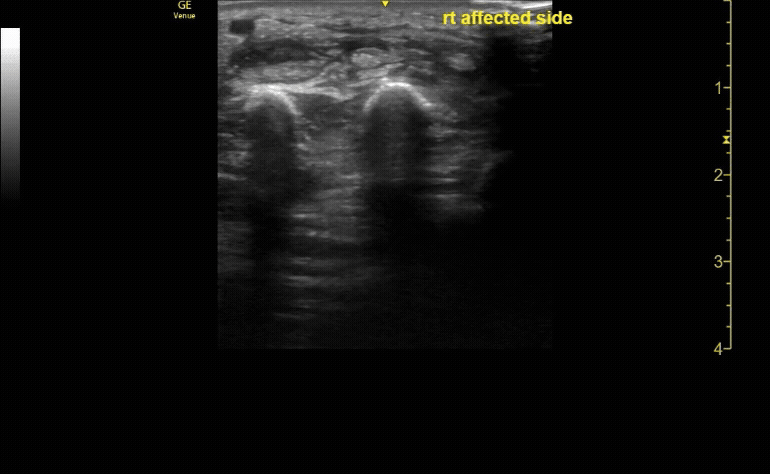
Affected tibia in transverse view.
c/o Santiago Tovar, MD
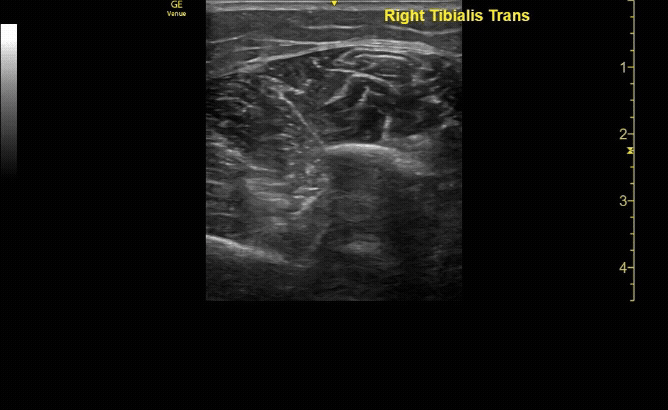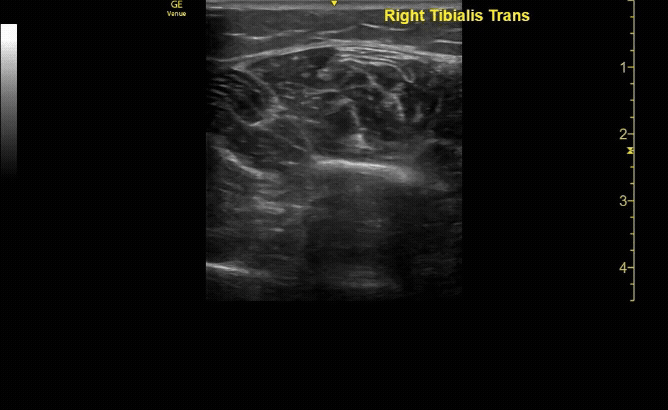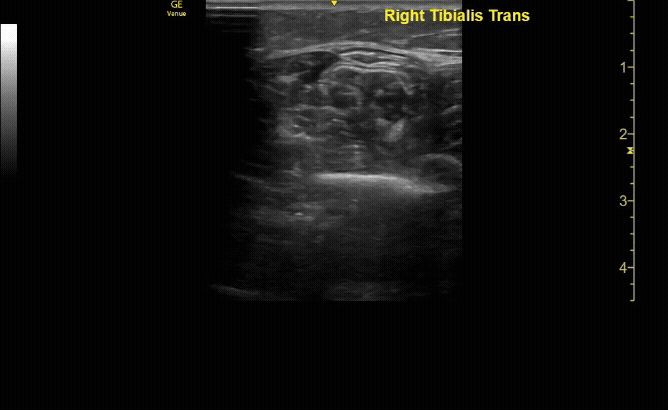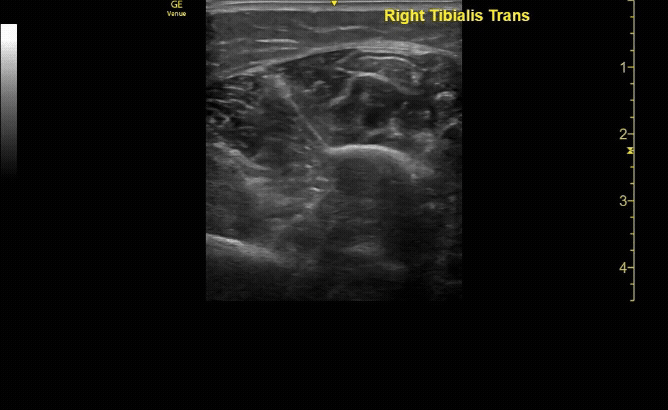
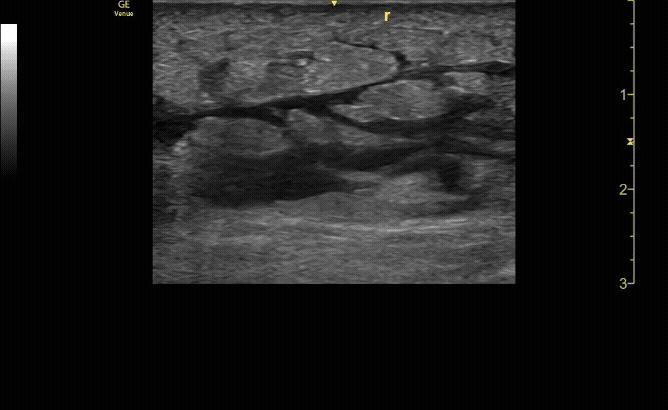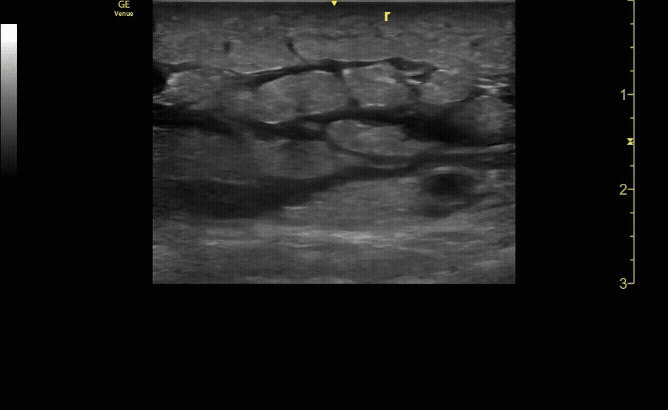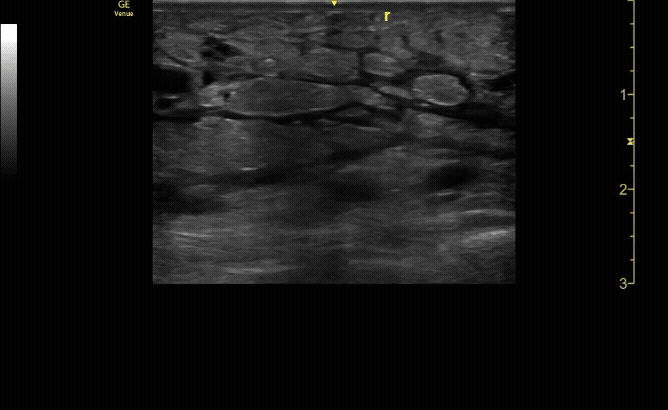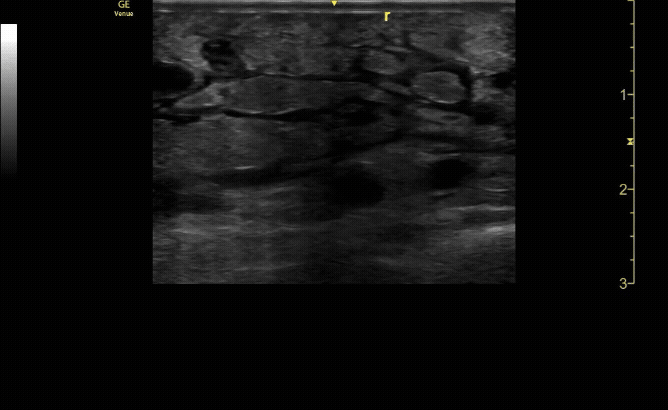
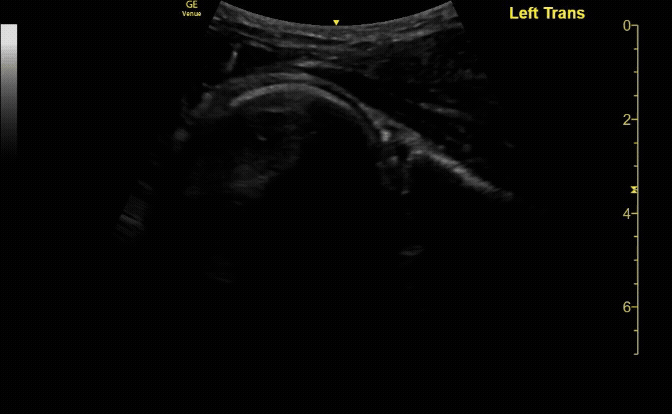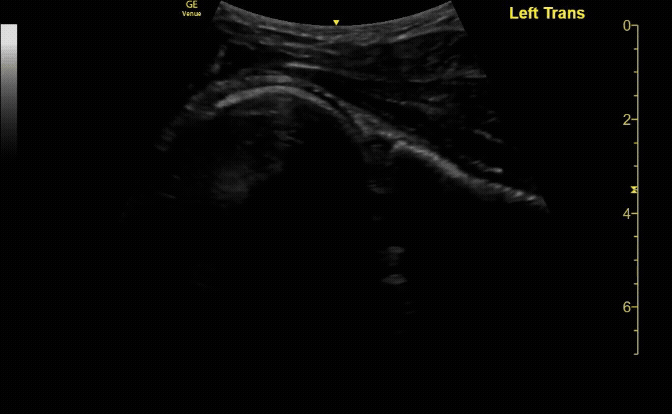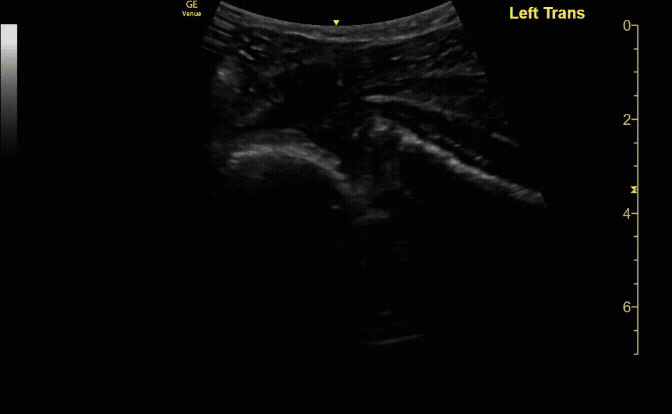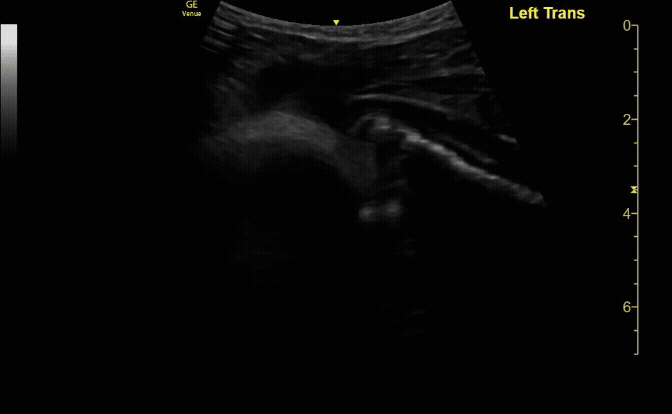
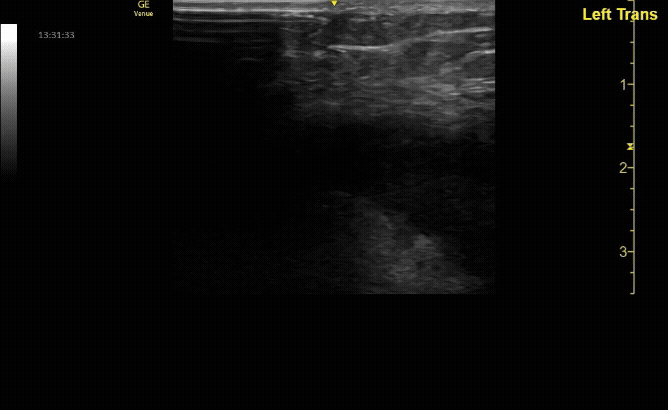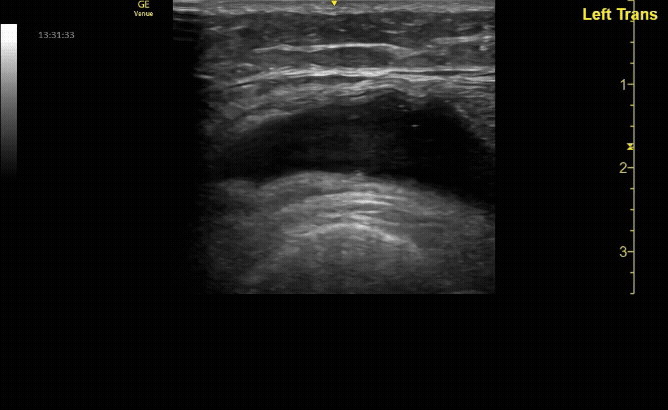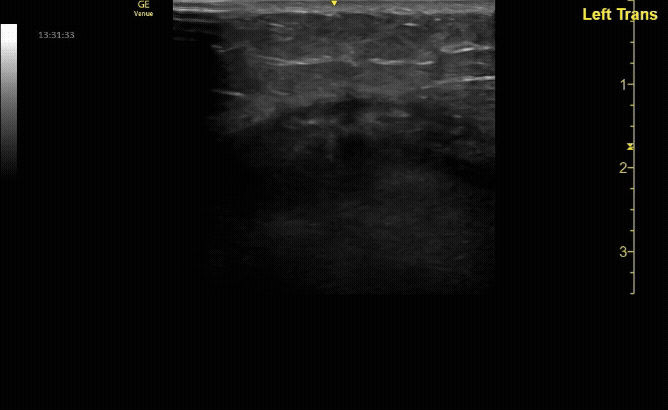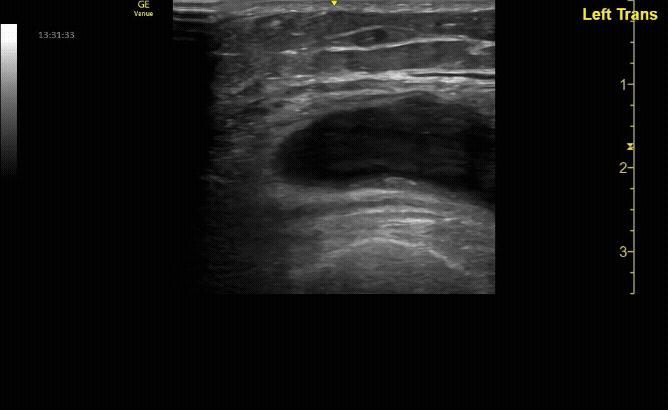
Affected tibia in sagittal view demonstrating displaced fracture.
c/o Santiago Tovar, MD
How to Scan:
ACEP Sonoguide: Soft Tissue Ultrasound
Core Ultrasound: MSK
POCUS 101: Shoulder Ultrasound Made Easy
ALiEM Educational Videos: Shoulder Dislocation Ultrasound Guided Injection
Taming the SRU - Musculoskeletal US
Tips/Tricks/Pitfalls:
Place the patient in a comfortable position so the area of concern is easily accessible
Do not skip the unaffected side, this gives a great reference for normal and abnormal
Utilize split screen to compare both sides simultaneously to more clearly visualize asymmetry and potential abnormalities
Recommend the linear probe for most indications, but in some cases the curvilinear probe may be more useful (deeper structures or joints)
Pathology:
Cobblestoning seen in a patient with cellulitis.
c/o Ibrahim Mansour, MD
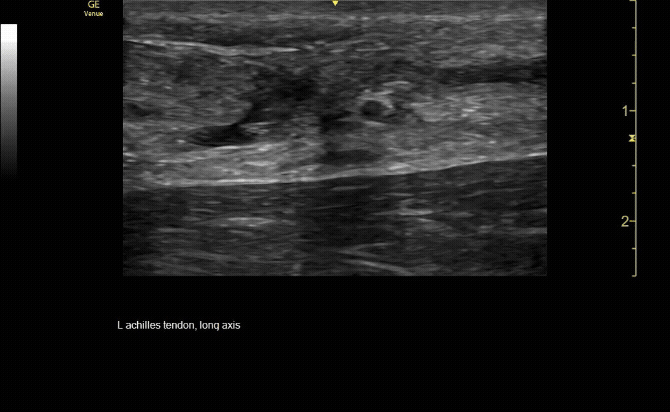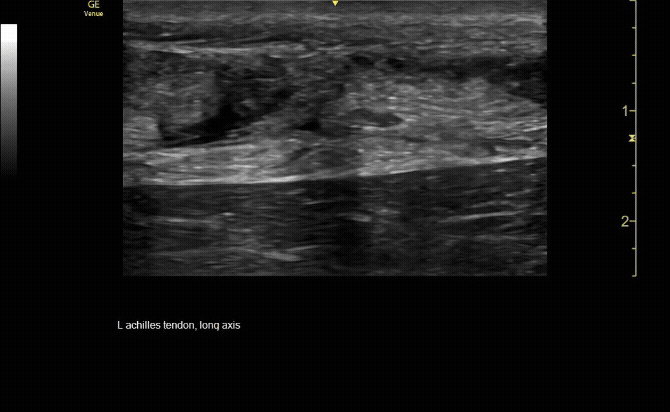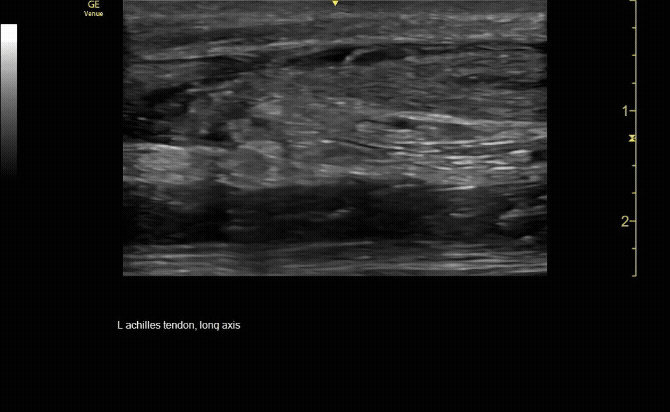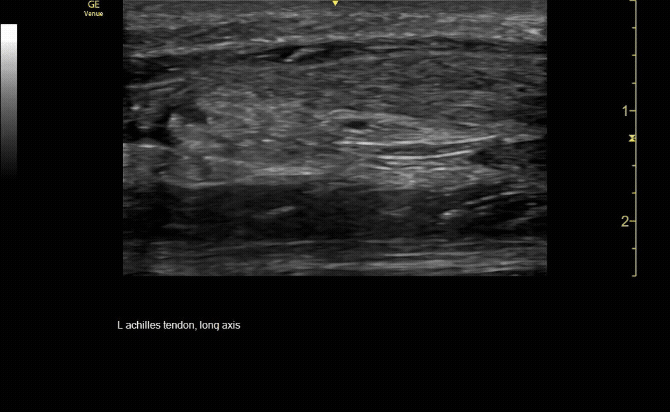
Sagittal view of achilles tendon rupture.
c/o Jasmine Hill, MD
Groin abscess.
c/o Katherine Aulis, MD
Extensor tenosynovitis in a patient following a cat bite.
Necrotizing fasciitis. Note air under the tendon.
c/o Adam Roussas, MD
Anterior shoulder dislocation/reduction.
c/o Victoria Gonzalez, MD
Wooden foreign body visualized with water bath.
c/o Samson Frendo, MD
Transverse view of knee effusion.
c/o Michael Dorritie, MD
Key Literature:
Schöll, et al Case Series: Ultrasound can be more informative than CT for radial head fractures
Haider et al. Evaluation of hand infections in the emergency department using POCUS
Additional Resources:
Malin and Dawson iBook Volume 1
Chapter 13: Joint Injections
Chapter 14: Hip
Chapter 15: Shoulder
Chapter 10: Soft Tissue
Chapter 11: MSK Basics
ACEP Imaging Compendium - Pages 35-40
The POCUS Atlas- MSK
AEUS Lecture Introduction to Musculoskeletal Ultrasound by Arthur Broadstock
Highland EM Ultrasound: Arthrocentesis
Author: Kathryn McGregor, MD (Class of 2026)
Reviewed by: Christine Jung, MD-FPD