Transabdominal First trimester oB
Learning Objectives:
Describe the indications, clinical algorithm, and limitations of transabdominal US in first-trimester pregnancy pain and bleeding
Identify relevant US anatomy including the cervix, uterus, adnexa, bladder and cul-de-sac
Perform US protocol for transabdominal views of the pelvic structures including uterus and ovaries, and obtain measurement of fetal heart rate and gestational age
Recognize the relevant findings for intrauterine avoid pitfalls for missing ectopic pregnancy:
Early embryonic structures including the gestational sac, yolk sac, fetal pole, and heart
Findings of ectopic pregnancy including pseudogestational sac, free fluid, and adnexal masses
Indications:
Evaluate for the presence of intrauterine pregnancy
Assess for gestational age, fetal cardiac activity, multiple gestations
Assess for free fluid exceeding an expected physiologic amount
Abdominal pain in early pregnancy or in person with uterus of childbearing age
Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy or in person with uterus of childbearing age
Extended Indications:
Directly identifying an ectopic pregnancy (versus recognizing there is no definitive IUP)
Ovarian cysts
Fibroids
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Required Views:
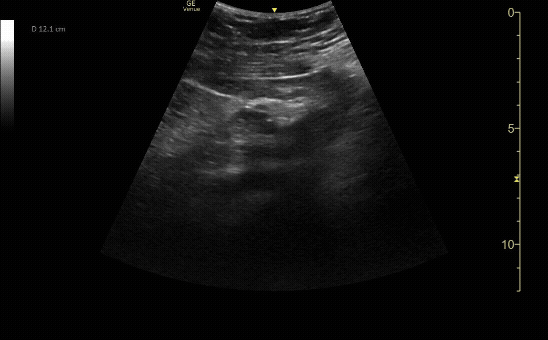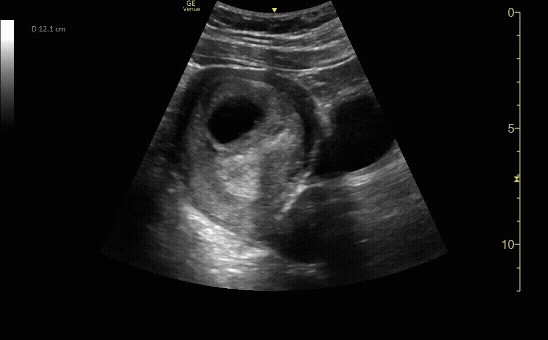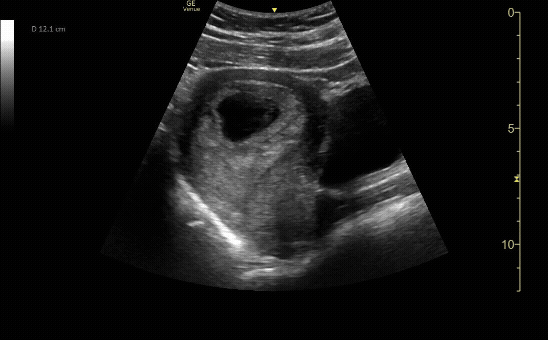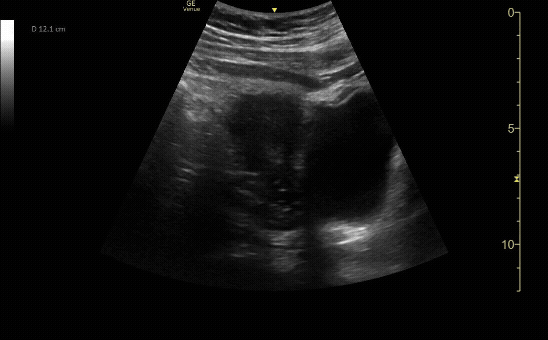
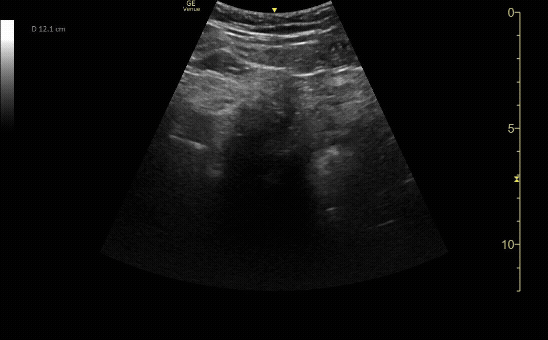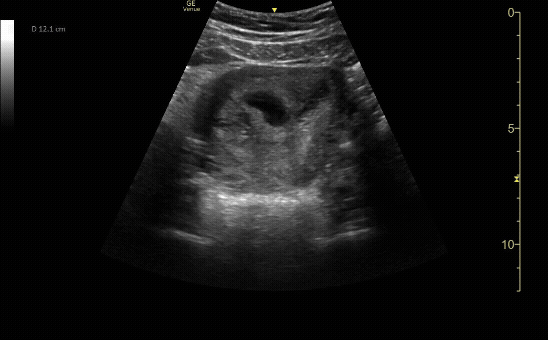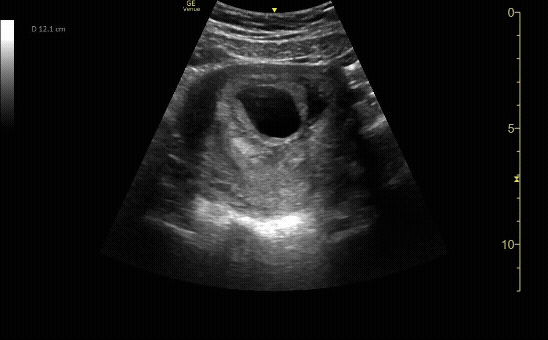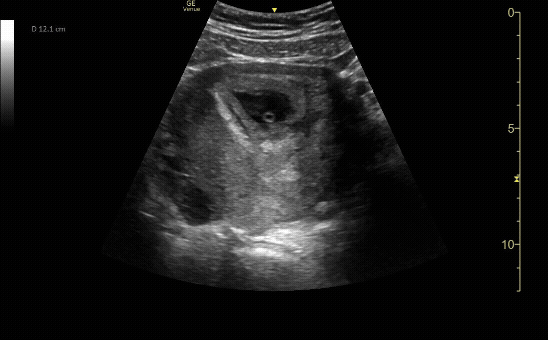
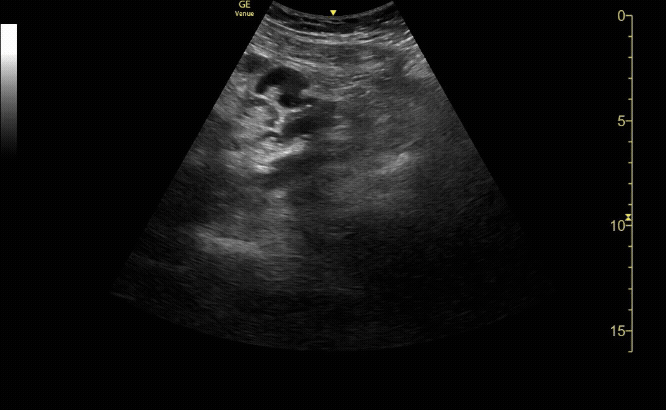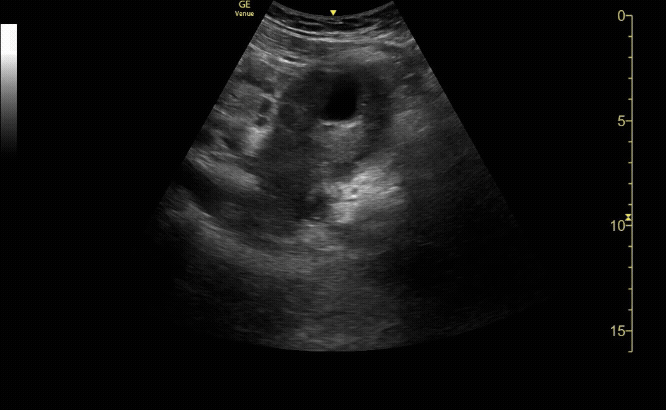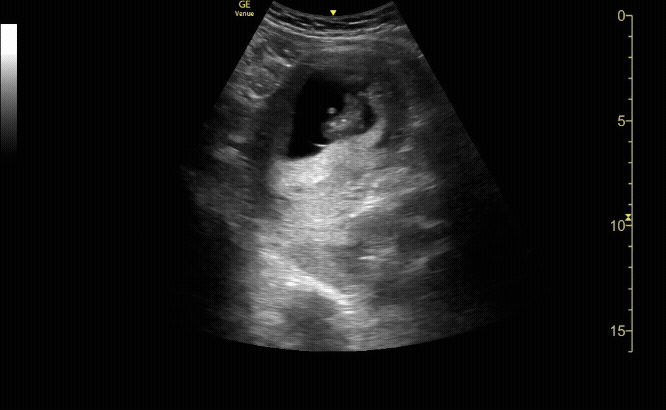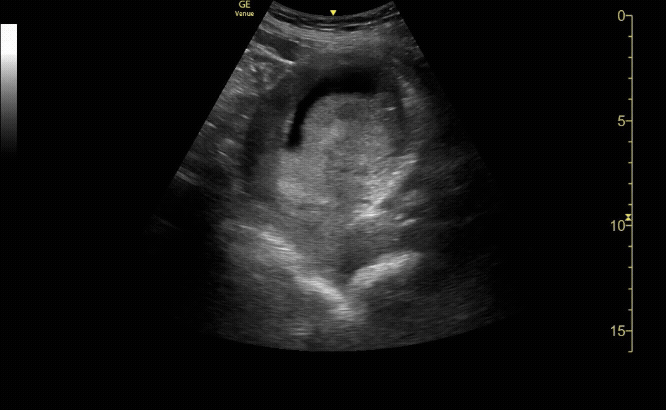
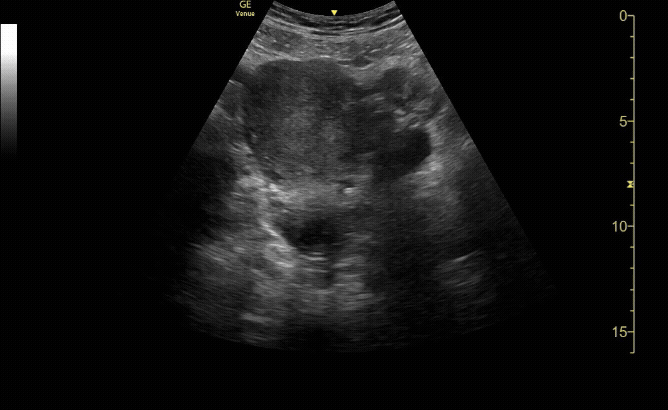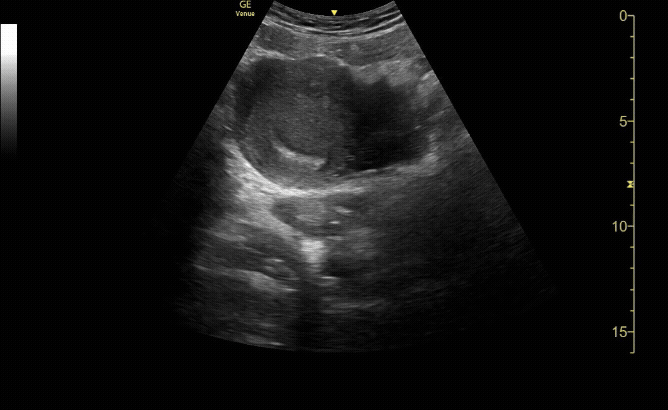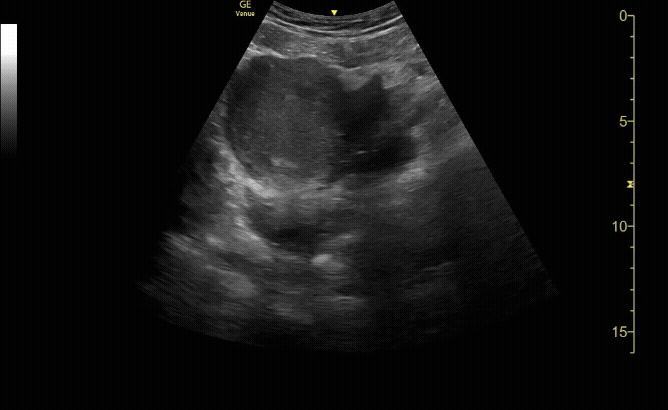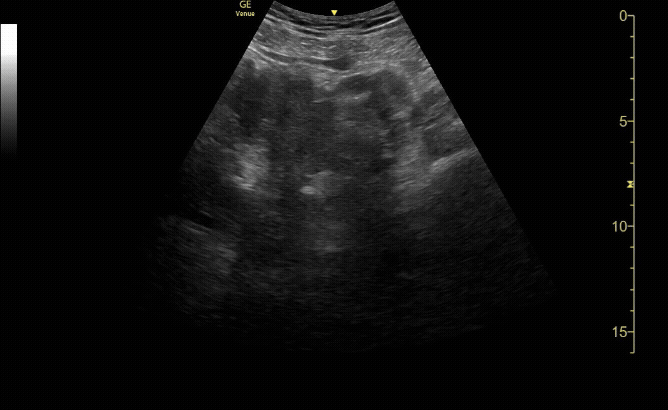
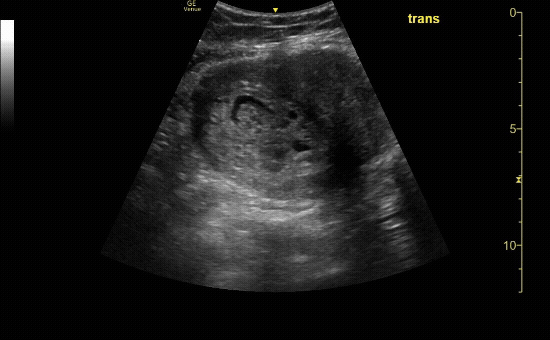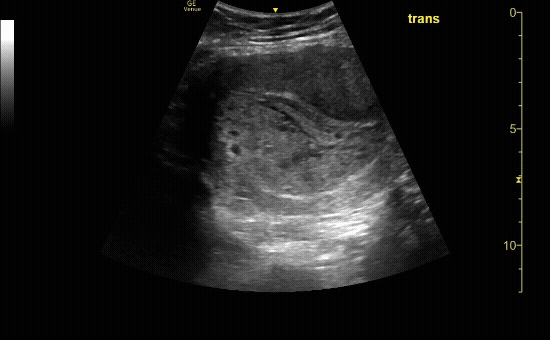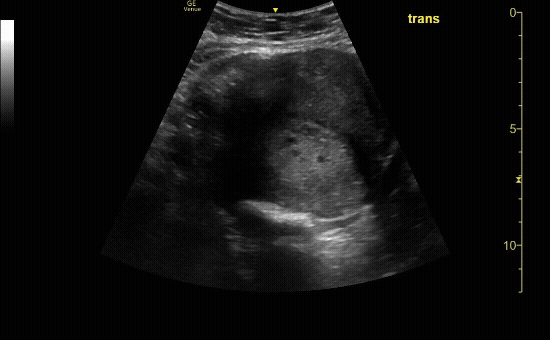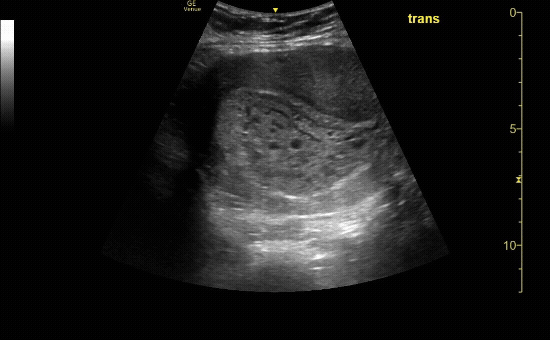
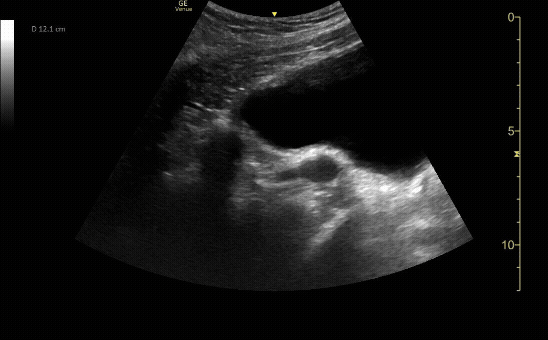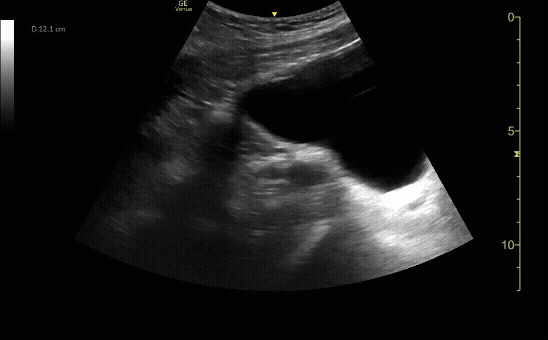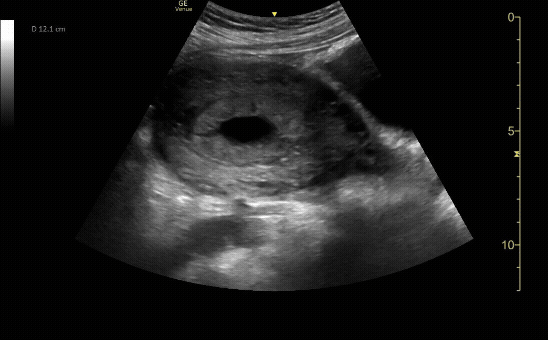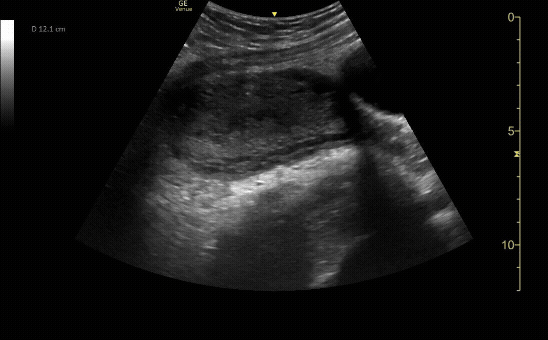
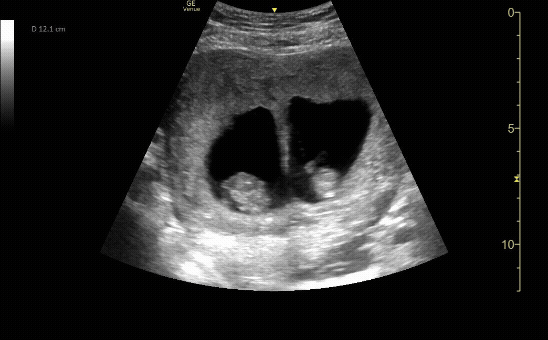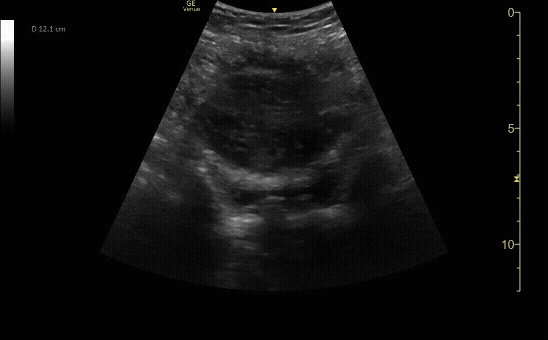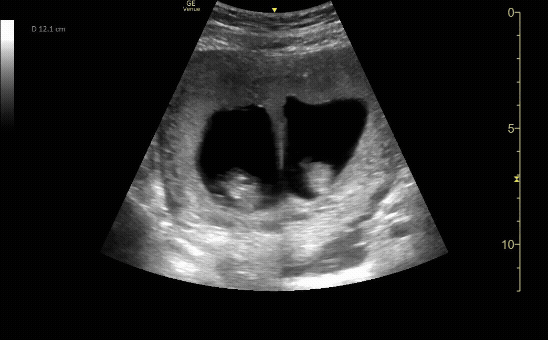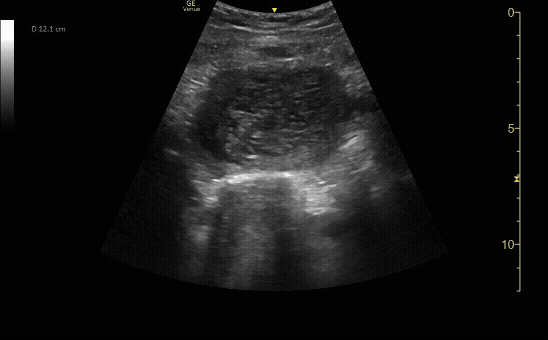
Sagittal view of the uterus with gestational sac, yolk sac, and fetal pole.
c/o Michael Hohl, MD
Transverse view of the uterus with intrauterine pregnancy.
c/o Michael Hohl, MD
Sagittal view of the uterus with fetal pole. Be sure to measure crown-rump length for credit.
c/o VIctoria Gonzalez, MD
M-Mode for measurement of fetal heart rate. Normal fetal cardiac rate in the first trimester is 110-180 BPM.
c/o Sohaib Amjad, MD
How to Scan:
ACEP Sonoguide: Early Pregnancy
POCUS 101: OB Ultrasound Made Easy
Tips/Tricks/Pitfalls:
Diagnosis of IUP requires the presence of a gestational sac containing a yolk sac (YS) in two planes within the endometrium which usually occurs around 5-6 weeks gestational age.
Identification of an IUP (in the absence of assisted reproductive therapy) by an emergency physician has a negative predictive value of 99.96% and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.08 for ruling out an ectopic pregnancy (1).
POCUS findings in early pregnancy:
4-6 weeks - gestational sac
5-7 weeks - yolk sac
6-8 weeks - fetal pole
No IUP + positive pregnancy test → perform a FAST exam to evaluate for free abdominal fluid suggestive of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy (especially in patient with hypotension, tachycardia)
Fluid in the center of the uterus can represent early gestational sac or can represent a pseudogestational sac, which is fluid caused by a decidual reaction in the center of the uterus in the setting of ectopic pregnancy.
As many as 1 in 10 ectopic pregnancies present with a pseudogestational sac.
An eccentrically located pregnancy <5-7mm from the edge of the myometrium is suspicious for an interstitial ectopic.
Ectopic pregnancies have been documented in the literature presenting well below traditional Beta hCG discriminatory thresholds, potentially as low as 30 IU/mL. In addition, a quantitative Beta hCG level cannot be utilized to rule out the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy.
A gestational sac in close approximation to the cervix or c-section scar should have comprehensive imaging performed.
Patients using assisted reproductive technology have a significant risk of developing a heterotopic pregnancy. ED providers should obtain a comprehensive US when evaluating these patients due to their risk of heterotopic pregnancy.
Retroverted or retroflexed uterine position can limit transabdominal exam. Providers enhance image quality by awaiting a full bladder, lying the patient flat, moving lateral to the midline, and applying gentle graded pressure.
Do not use color doppler when evaluating first trimester pregnancy – the increased acoustic output of spectral doppler ultrasound can be harmful to the early pregnancy
Detection of congenital or fetal anomalies is outside the scope of POCUS. Patients should be informed that POCUS does not supersede or replace routine obstetric care and imaging.
Pathology:
Transverse view of the uterus with no IUP and a left adnexal mass consistent with early ectopic pregnancy
c/o Victoria Gonzalez, MD
Transverse view of the uterus with molar pregnancy.
c/o Ramin Chitsaz, MD
Sagittal view of the uterus with IUP and small subchorionic hemorrhage.
c/o Leslie Cachola MD
Transverse view of the uterus with twin gestation at 10-12 weeks.
c/o Ala’a Abu-Spetani, MD
Key Literature:
Additional Resources:
Malin and Dawson iBook Volume 1 , Chapter 7: Pregnancy
ACEP Emergency Ultrasound Imaging Criteria Compendium Pages 26-29
The Ohio State University guide on Pelvic US
AliEM's 4 Pitfalls of Bedside Ultrasonography During First Trimester Pregnancy
Emergency Ultrasound by Geoff Hayden
Author: Priyanka Pradhan, MD (Class of 2026)
Reviewed by: Victoria Gonzalez, MD FDP-AEMUS